Figure 2.
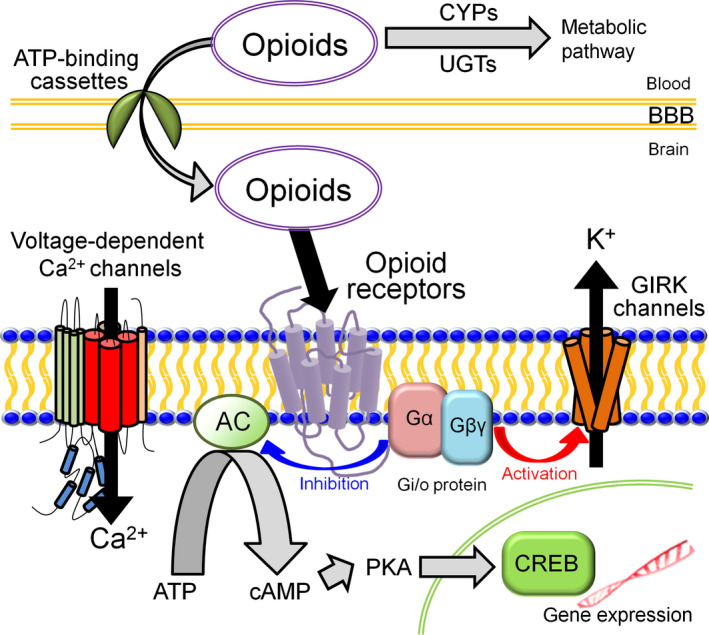
Molecules associated with the action of opioid analgesics. The analgesic effects of opioids depend on such factors as opioid peptide receptors, effector molecules, metabolic enzymes, and transporters. The effector molecules are affected by Gi/o protein include G protein‐activated inwardly rectifying potassium (GIRK) channels, voltage‐dependent Ca2+ channels, and adenylyl cyclase (AC), which influence the activity of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)‐responsive element‐binding protein (CREB) through the actions of cAMP and protein kinase A. The metabolic enzymes include cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs) and UDP‐glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs). The transporters include adenosine triphosphate (ATP)‐binding cassettes
