Fig 3. Risk of bias showing review authors' judgement about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
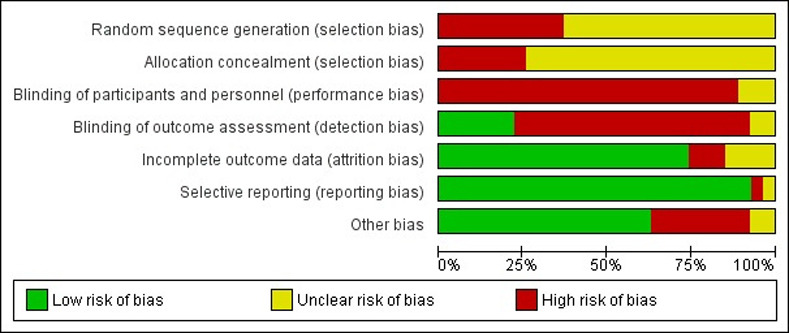
The following methodological domains based on RoB were evaluated. Consider selection bias: “Was the allocation sequence adequately generated and applied?”, “Were the groups similar at baseline or were they adjusted for confounders in the analysis?”, “Was the allocation to the different groups adequately concealed?”; Consider performance bias: “Were the animals randomly housed during the experiment?”, “Were the caregivers and/or investigators blinded from knowledge regarding which intervention each animal received during the experiment?”; Consider detection bias: “Were animals selected at random for outcome assessment?”, “Was the outcome assessor blinded?”; Considers attrition bias: “Were incomplete outcome data adequately addressed?”; Considers reporting bias: “Are reports of the study free of selective outcome reporting?”; Considers other biases: “Was the study apparently free of other problems that could result in high risk of bias?”; The overall study quality indicators: “Was it stated that the experiment was randomized at any level?” and “Was it stated that the experiment was blinded at any level?”. The items in the RoB tool were scored with “yes” (low risk of bias); “no” (high risk of bias); or “unclear” (indicating that the item was not reported, and therefore, the risk of bias was unknown) [12]. The items in the RoB tool were scored with “yes” (low risk of bias); “no” (high risk of bias); or “unclear” (indicating that the item was not reported, and therefore, the risk of bias was unknown) [17].
