Fig. 3.
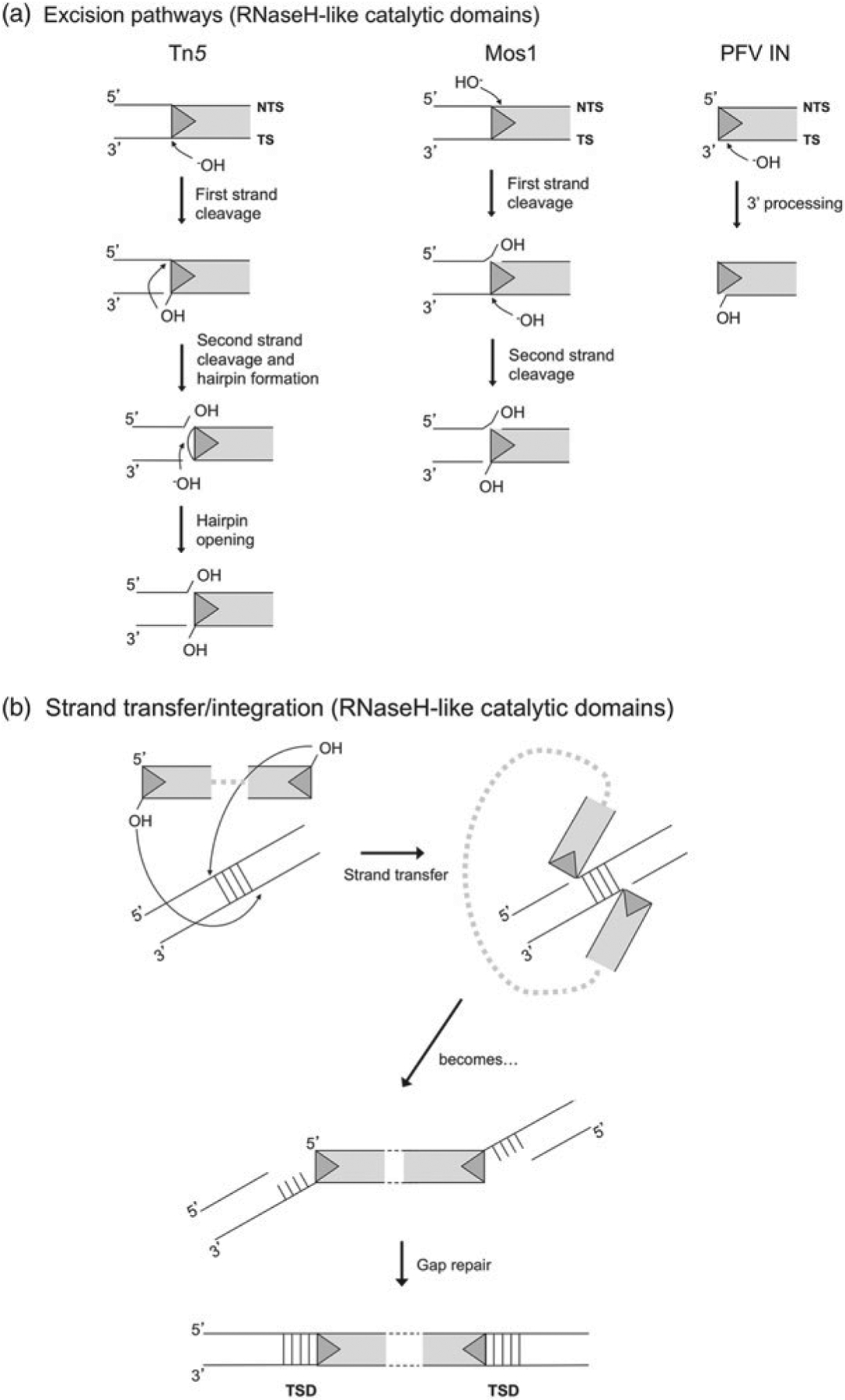
(a) Excision pathways for Tn5, Mos1, and PFV integrase. Only reactions occurring on the TE LEs are shown. For Tn5, cleavage on both the NTS and the TS occur precisely at the transposon end. For Mos1, NTS cleavage occurs three bases within the transposon end and TS cleavage is precisely at the transposon end. For retroviral integrases such as that of PFV, the product of reverse transcription is a blunt-ended provirus from which integrase removes two 3′-OH nucleotides from the TS in a step known as 3′-processing. (b) Strand transfer pathway for DDE transposases. Shown is the specific pathway for PFV integrase, which catalyzes concerted integration into target DNA with a 4 bp stagger. As a result, after gap repair, the TE is flanked on both sides by a 4 bp TSD. For Tn5, staggered sites for strand transfer are offset by 9 bp and for Mos1 by 2 bp.
