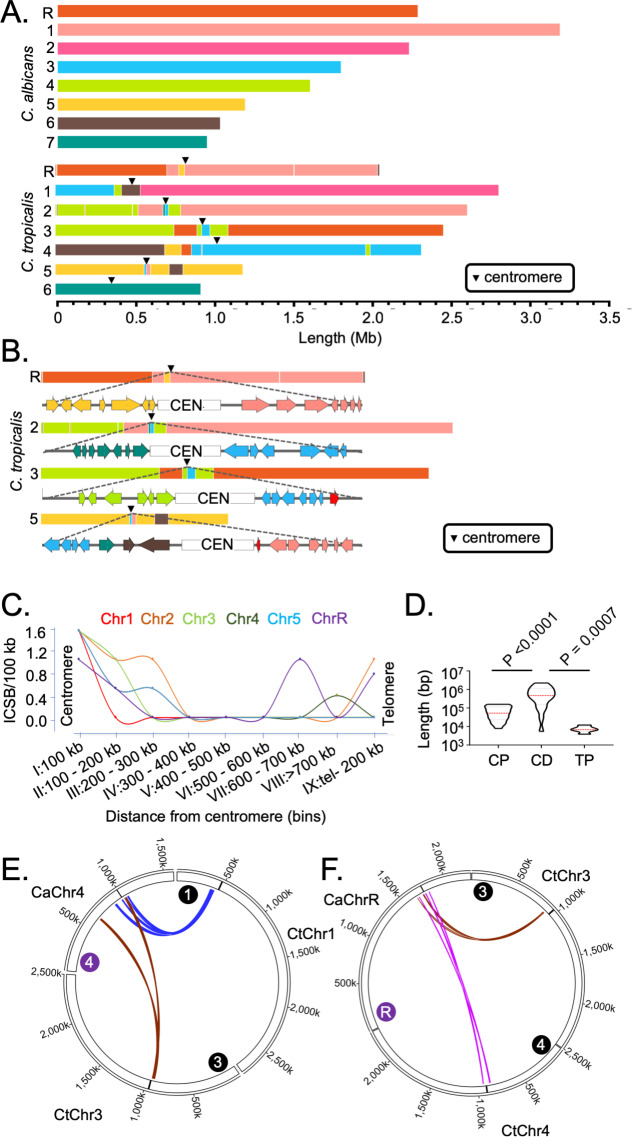
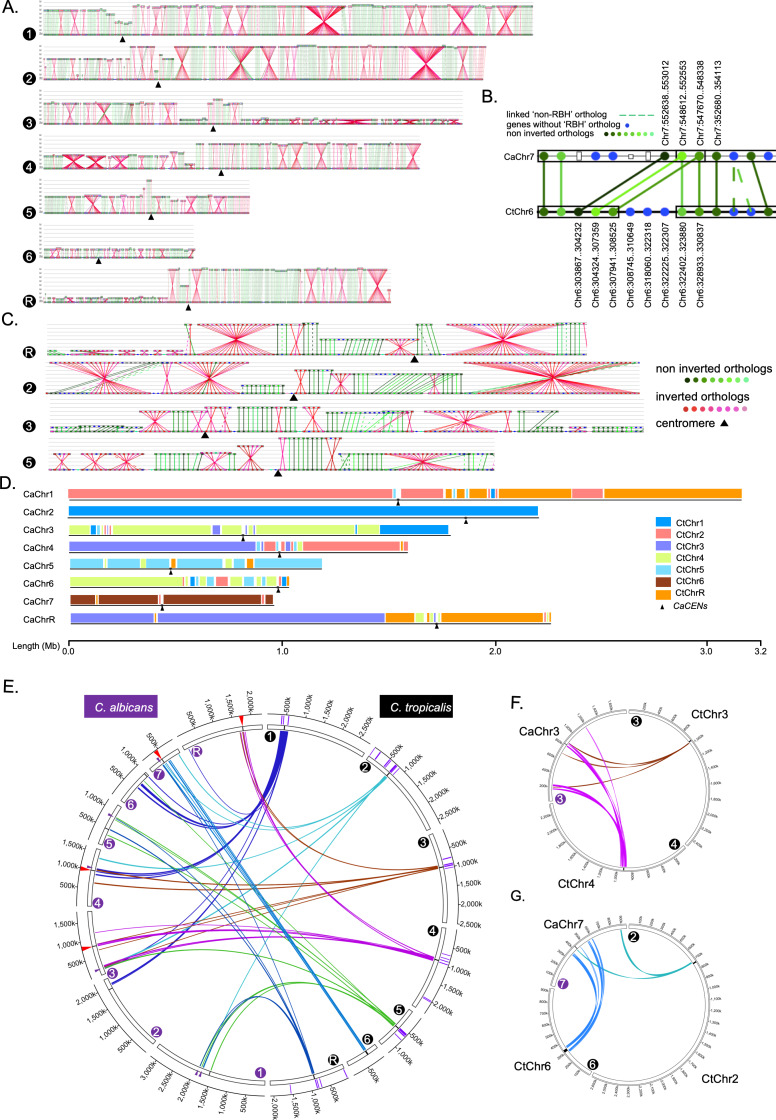
Figure 3. Genome-wide mapping of interchromosomal synteny breakpoints in C. tropicalis identifies a spatial cue for karyotype evolution.
(A) Scaled representation of the color-coded orthoblocks (relative to C. albicans chromosomes) and ICSBs (white lines) in C. tropicalis (Materials and methods). Orthoblocks are defined as stretches of the target genome (C. tropicalis) carrying more than two syntenic ORFs from the same chromosome of the reference genome (C. albicans). The centromeres are represented with black arrowheads. (B) Zoom in view of the C. tropicalis centromere-specific ICSBs on CEN2, CEN3, CEN5 and CENR showing the color-coded (relative to C. albicans chromosomes) ORFs flanking each centromere. C. tropicalis-specific unique ORFs proximal to CEN3 and CEN5 are shown in red. (C) A plot showing the chromosome-wise ICSB density, calculated as number of ICSBs per 100 kb of the C. tropicalis genome (y-axis), as a function of the linear distance from the centromere in nine bins. These bins are a) 0–100 kb on both sides of centromere (bin I), (b) 100–200 kb (bin II), (c) 200–300 kb (bin III), (d) 300–400 kb (bin IV), (e) 400–500 kb (bin V), (f) 500–600 kb (bin VI), (g) 600–700 kb (bin VII), (h) >700 kb to 200 kb from telomere ends (bin VIII), and i) 200 kb from the telomere ends (bin IX). Chr6 was excluded from this analysis, as it does not harbor any ICSB. (D) A violin plot comparing the distribution of lengths of orthoblocks (y-axis) at three different genomic zones: a) the centromere-proximal zone (CP), (b) the centromere-distal zone (CD), and c) telomere-proximal zone (TP). Orthoblocks, which span over more than one zone, were assigned to the zone with maximum overlap. The centromere-distal dataset was compared with the other two groups using the Mann-Whitney U test and the respective P values are mentioned. (E - F) Circos plots representing the convergence of centromere-proximal ORFs of C. tropicalis chromosomes near the centromeres (CEN4 and CEN7) of C. albicans. Chromosomes of C. tropicalis and C. albicans are marked with black and purple filled circles at the beginning of each chromosome, respectively.