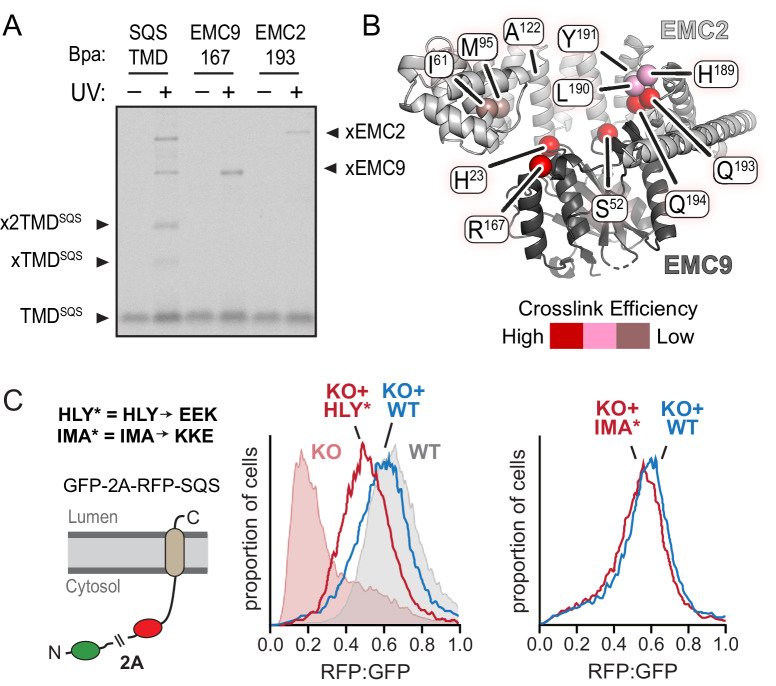
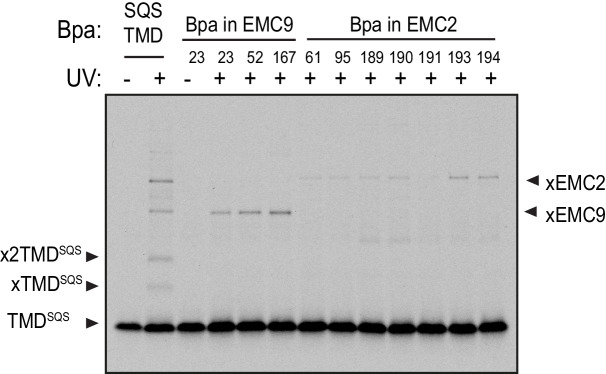
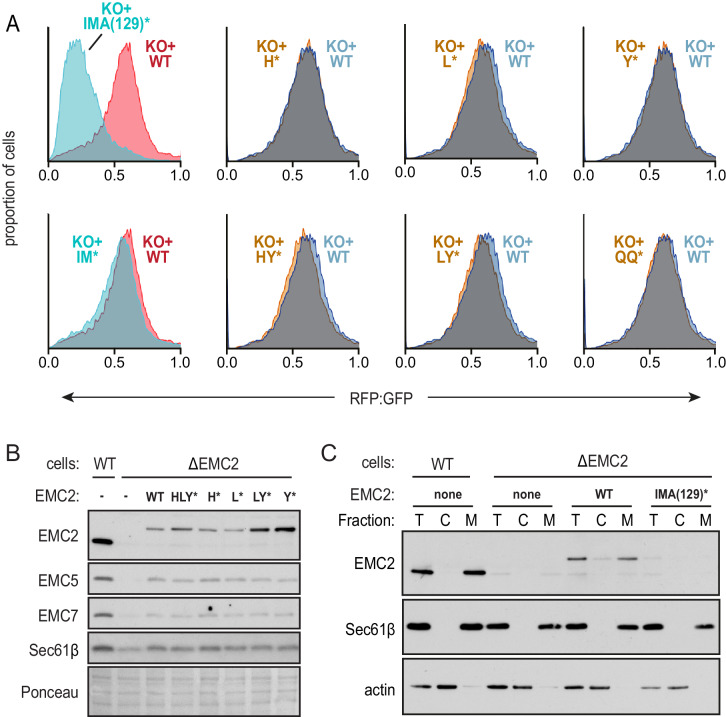
Figure 3. Functional analysis of the EMC2•EMC9 cytosolic vestibule.
(A) 35S-methionine-labeled TMD of SQS was mixed with recombinant purified EMC2•EMC9 complex as in Figure 1 and analyzed directly or after UV irradiation as indicated. The photocrosslinking amino acid benzoyl-phenylalanine (Bpa) was incorporated into either the SQS substrate, EMC9 (at codon 167), or EMC2 (at codon 193) as indicated. Both R167 in EMC9 and Q193 in EMC2 line the vestibule. (B) Bpa was incorporated at different positions within the vestibule of the EMC2•EMC9 complex and crosslinking efficiency to SQS was determined as in panel A. Locations of the Bpa are annotated as spheres on the EMC2•EMC9 heterodimer. The sphere colors correspond to the intensity of the resulting crosslink. Position 191 (obscured behind L190 in this view) showed no crosslinking to substrate, consistent with its rearward facing location. (C) Shown on the left is a diagram of the dual color reporter for insertion of the TMD of SQS. Expression of this reporter results in a free GFP protein and an RFP-tagged SQS protein due to ribosomal skipping at the a viral 2A sequence. The left graph shows flow cytometry analysis of the SQS reporter in WT cells (grey), EMC2 knockout (KO) cells (shaded pink), KO cells complemented with WT EMC2 (blue line), and KO cells complemented with the HLY* EMC2 mutant (red line). The data are represented as histograms of the RFP to GFP ratio. The right graph shows a comparison of the SQS reporter in KO cells complemented with either WT EMC2 or the IMA* EMC2 mutant. The mutated amino acids, whose positions are shown in panel B, are: H189E, L190E, Y191K, I61K, M95K, and A122E.