Figure 1.
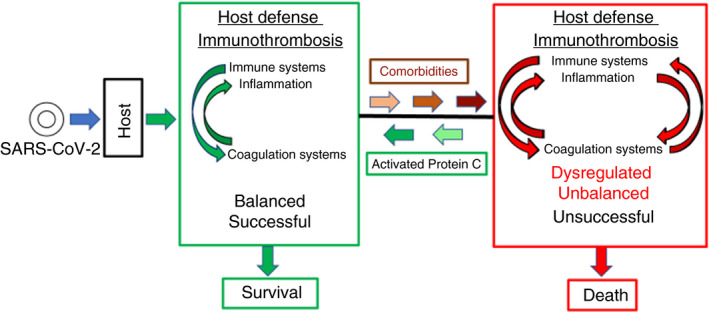
COVID‐19: balanced host defense versus unbalanced, dysregulated host defense. SARS‐CoV‐2 infection triggers host defense, which comprises multiple subsystems including, among others, the innate immune system and the blood coagulation systems, which reciprocally activate each other to attack and help neutralize the virus with integration from other host defense subsystems. The crosstalk and integration of molecular and cellular defense mechanisms for these 2 subsystems may be termed immunothrombosis or thromboinflammation. 7 , 8 , 9 Provided that the inflammatory reactions and the coagulation reactions are appropriately regulated by both positive and negative feedback loops, host defense is successful, resulting in rejection of the invader and survival of the host. However, when one or more of the host defense subsystems is less responsive or already chronically hyperactivated (eg, inflammatory condition, hypercoagulable state, etc) due to comorbidities such as cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, diabetes, and so on, then the normal regulatory processes of host defense subsystems are unbalanced. As observed in seriously ill patients with COVID‐19, biomarkers for dysregulated, excessively active immune system include markedly elevated cytokines and chemokines and, for excessive blood coagulation, D‐dimer reflecting fibrin formation and fibrinolysis. The net result of such comorbidities can be that the inflammatory reactions and the coagulation reactions are dysregulated and excessive, resulting ultimately in death. APC provides multiple cytoprotective activities and, in preclinical studies, APC’s cell‐signaling actions attenuate many types of injuries and reduces death from bacterial pneumonia. Thus, it is hypothesized that the recombinant signaling‐selective 3K3A‐APC protein will help counteract the dysregulation of immunothrombosis that can arise in the course of host defense against the SARS‐CoV‐2 virus and will increase the probability for survival of severely ill COVID‐19 patients. APC, activated protein C; COVID‐19, coronavirus disease 2019; SARS‐CoV‐2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
