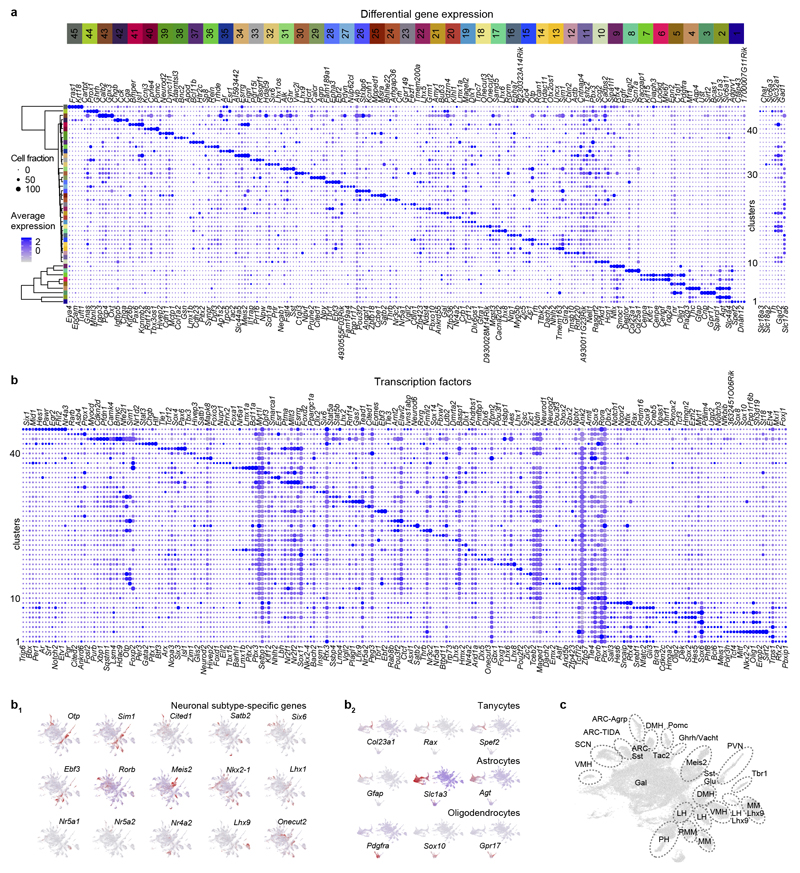
ED Figure 1. Marker genes to define molecular phenotypes.
(a) Differential gene expression by glia (#1-9) and neurons (#10-45). Because of the integration of six stages, early-expressed TFs and spatially-restricted genes amenable to cellular differentiation were identified. For neuronal clusters, fast neurotransmitter specificity is shown to the right. Relative diameter of the solid circles for each cluster is scaled to the fraction of cells that expresses a specific gene. Color coding and numbering at the top correspond to those in Figure 1a. (b) Dot plot representation of differential TF expression in 45 ectoderm-derived cell groups in the hypothalamus. (b1,b2) Subclass-specific TFs recapitulate the UMAP positions of neuronal (b1) and tanycyte (b2) subtypes. (c) Integrated molecular/anatomical annotation of hypothalamic with their specific assignment to hypothalamic areas. Abbreviations: ARC-Agrp, arcuate nucleus-agouti-related peptide+ neurons; ARC-Sst, arcuate nucleus-somatostatin+ neurons; ARC-TIDA, arcuate nucleus-tuberoinfundibular dopamine neurons; DMH, dorsomedial hypothalamus; Gal, galanin; Ghrh/Vacht, growth hormone-releasing hormone/vesicular acetylcholine transporter+ neurons; LH, lateral hypothalamus; LH-Lhx9, lateral hypothalamus-LIM homeobox 9+ cluster; Meis2, meis homeobox 2; MM, ; MM-Lhx9, mammillary nucleus-LIM homeobox 9+ neurons; Pomc, proopiomelanocortin; PH, posterior hypothalamus; PMM, premamillary nucleus; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; SCN, suprachiasmatic nucleus; Tbr1, T-box brain transcription factor 1; VMH, ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus.