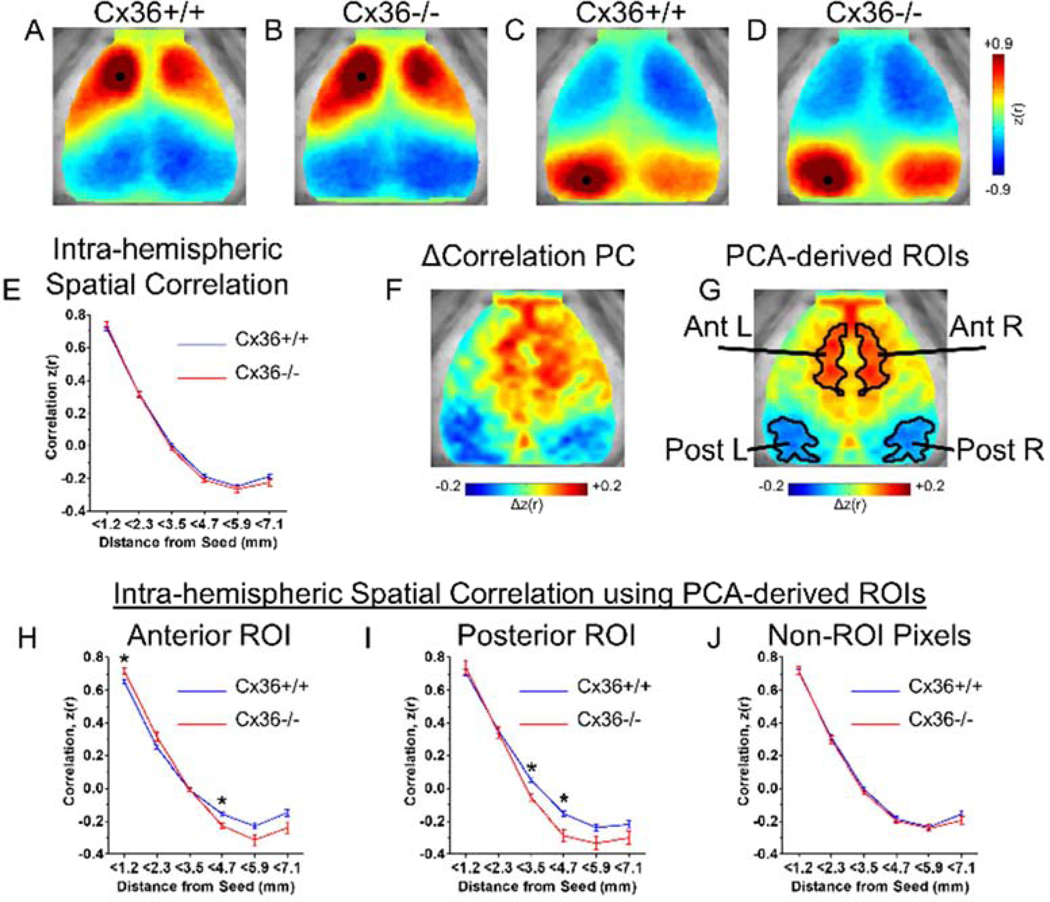
Figure 1.
Cx36 deletion altered spatial ISA correlation relationships in specific cortical regions. (A–D) Group averaged seeded correlation maps for (A,B) an anterior seed and (C,D) a posterior seed. Consistent with previous studies, all maps showed high correlation surrounding the seed, high homotopic correlation, and anterior-posterior anti-correlation. Qualitatively, the Cx36−/− mice have increased correlation values near the seed. (E) Group averaged correlation values vs. distance for every intra-hemispheric pixel. For each mouse, the correlation vs. distance curve from the left and right hemisphere was averaged before group averaging was performed. Using a subset of mice (Cx36+/+ n=3, Cx36−/− n=3), PCA was performed on the correlation differences between groups in order to find ROIs that may be selectively influenced by Cx36. (F) The first principal component derived from Δcorrelation PCA reveals distinct anterior and posterior ROIs with ISA correlation patterns that differ between Cx36+/+ and Cx36−/− groups. (G) Anterior and Posterior ROIs defined after smoothing, bilateral averaging, and thresholding of the Δcorrelation PC in (F). These ROIs were used for analysis on an independent set of mice (Cx36+/+ n=16, Cx36−/− n=10). (H–J) Spatial correlation values for pixels within the ROIs from (G). (H) Within the anterior ROI, Cx36 deletion caused increased correlation for nearby pixel pairs (<1.2mm), and increased anti-correlation for more distant pixel pairs (3.5mm–4.7mm). (I) Within the posterior ROI, Cx36 deletion resulted in increased anti-correlation at further distances (3.5mm–4.7mm). The correlation vs. distance curve was calculated between all pixels within the ROIs and every other pixel in the same hemisphere. (J) Correlation vs. distance relationship for pixels outside of the ROIs from (G). No differences were found for pixels in this area. *P<0.0083 (0.05/number of distance bins; determined using Student’s t test with Bonferonni correction).