FIG. 3.
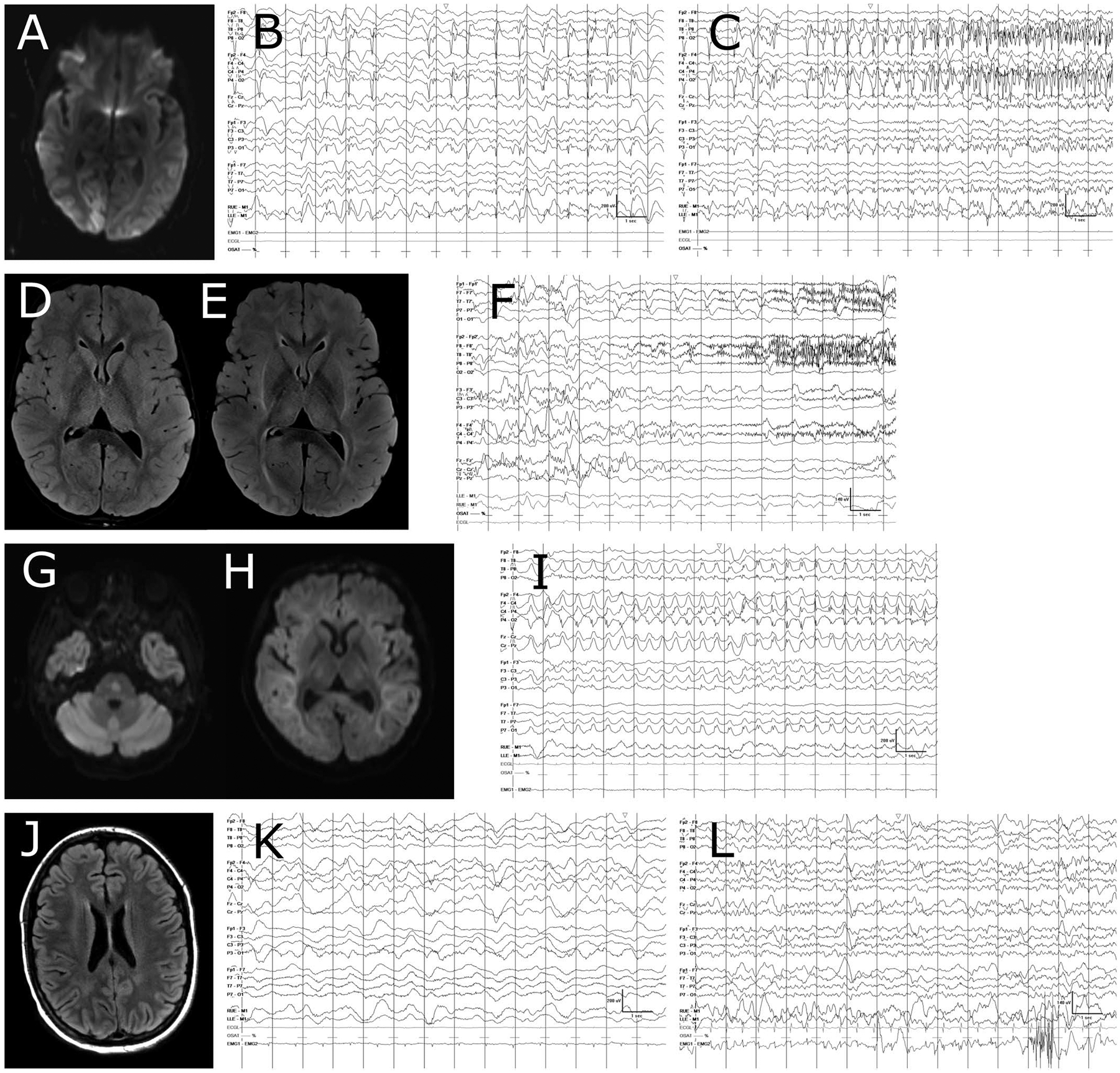
MRI and EEG findings during neurotoxicity. Selected cases are shown, with subject ID numbers corresponding to Table 3. A–C, Subject 1. A, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) showing R > L occipital cortical diffusion restriction. B, Shows lateralized periodic discharges without evolution in frequency or field, which were present for several days on cEEG. In (C), onset of a seizure from the background of periodic discharges is shown. D–F, Subject 4. D, Shows fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequence obtained on day 6 after CAR T cell infusion. There is mild edema in the bilateral thalami and subtle white matter signal abnormalities. E, Shows the same sequence on day 9, with more prominent white matter FLAIR signal and more pronounced bithalamic edema. This change in imaging was accompanied by a worsening of EEG background toward a more discontinuous pattern. F, Shows left-sided periodic discharges, and a seizure with fast activity arising from the right hemisphere at the same time. The seizure had clinical manifestations of left upper extremity shivering. G-I, Subject 5. G, DWI sequence showing diffusion restriction in the pons. H, DWI sequence showing extensive diffusion restriction throughout the supratentorial white matter, with relative sparing of the cortex. I, Shows the evolution of a typical focal seizure for this subject. J-L, Subject 2. J, FLAIR sequence showing mild diffuse supratentorial white matter T2 hyperintensities, which were not present on MRI before CAR T cell treatment. K, Mildly asymmetric slow wave pattern, the patient was comatose without sedation at the time of this recording. L, EEG obtained 9 days later, at which time the patient was awake and alert, but having difficulty answering orientation questions. EEG grid lines represent 1 second intervals. CAR, Chimeric Antigen Receptor.
