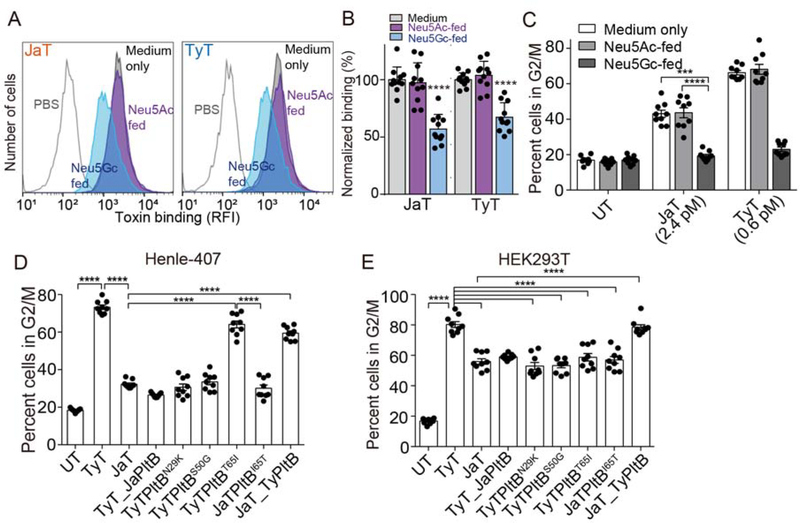
Figure 4. The Role of PltB Amino Acid Sequence Variations in Glycan Binding Preferences and Virulence Outcomes.
A-B, Toxin binding analysis of Henle-407 cells fed with either Neu5Gc or Neu5Ac. Shown are representative flow histograms (A) and quantification (B). C, Toxicity assays of cells that correspond to A and B. D-E, Cell cycle profile analysis of Henle-407 cells (D) and HEK293T (E) treated with indicated toxin preparations. UT, untreated; TyT, typhoid toxin; JaT, Javiana toxin; TyT_JaPltB, a typhoid toxin mutant containing Javiana toxin PltB subunits; TyTPltBN29K, TyTPltBS50G, and TyTPltBT651; typhoid toxin mutants containing singly substitution to amino acids found on Javiana toxin PltB; JaTPltBI65T, a Javiana toxin mutant containing I65T substitution; JaT_TyPltB, a Javiana toxin mutant containing Typhoid toxin PltB subunits. At least three independent experiments were performed. Bars represent average ± standard deviation. ***, p<0.001, ****, p<0.0001. Two-tailed unpaired t-tests were used for B-E. See also Figure S2–S3 and Table S2–S3.