Figure 1. Schematic diagram of vertebrate complement cascades and the particular steps Lyme borreliae anti-complement protein interact.
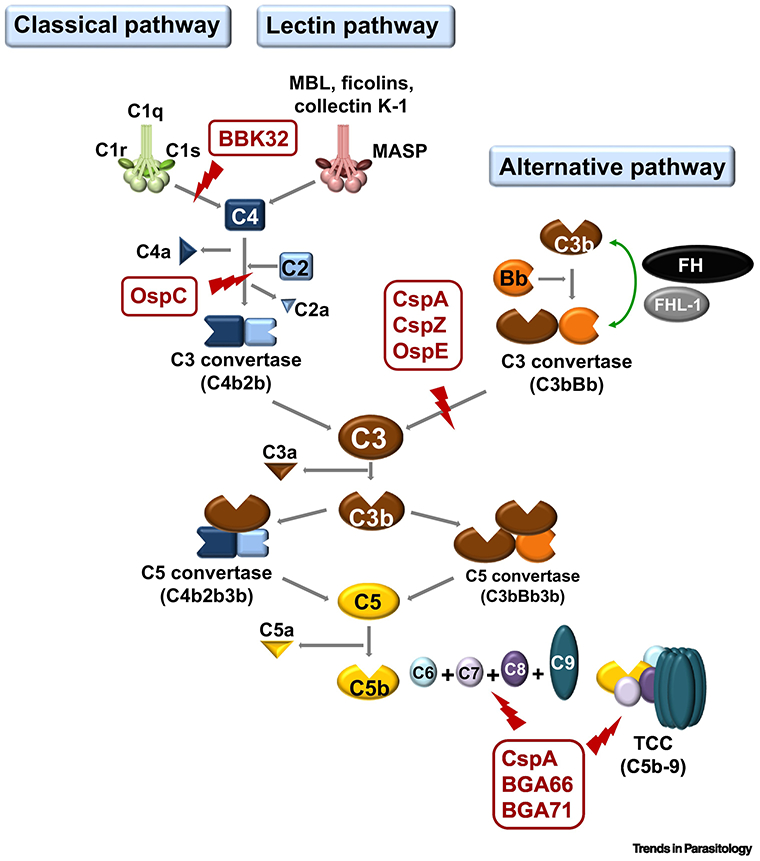
The CspA, CspZ, and OspE of B. burgdorferi s.l. target the host complement regulator, FH, by inhibiting the formation C3bBb to inactivate AP. LD spirochetes also produce BBK32 and OspC that bind to C1r and C4b, respectively. These proteins inhibit CP (for BBK32 and OspC) and LP (for OspC). Additional proteins of B. burgdorferi s.l. (e.g. CspA, BGA66, and BGA71) inactivate TCC by preventing the formation of C5b-9 on the surface of spirochetes (Part of the figure is adapted from [18]). FH, Factor H; AP, alternative pathway; CP, classical pathway; LP, Lectin pathway; TS, terminal sequence; LD, Lyme disease; TCC, terminal complement complex
