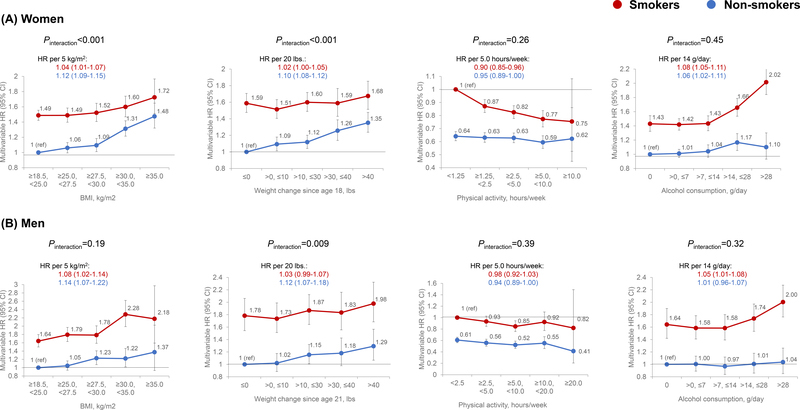
Figure 1.
Associations of BMI, weight change, physical activity, and alcohol intake with incidence of total carcinoma according to smoking status in women (A) and men (B). Multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression was used to calculate the hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) after adjusting for age, calendar year, family history of cancer, pack-years of smoking, multivitamin use, and regular use of aspirin. In addition, we performed mutual adjustment for BMI, alcohol, and physical activity; and adjusted for body weight at 18 years for women and 21 for men for the analysis on weight change.