Figure 6.
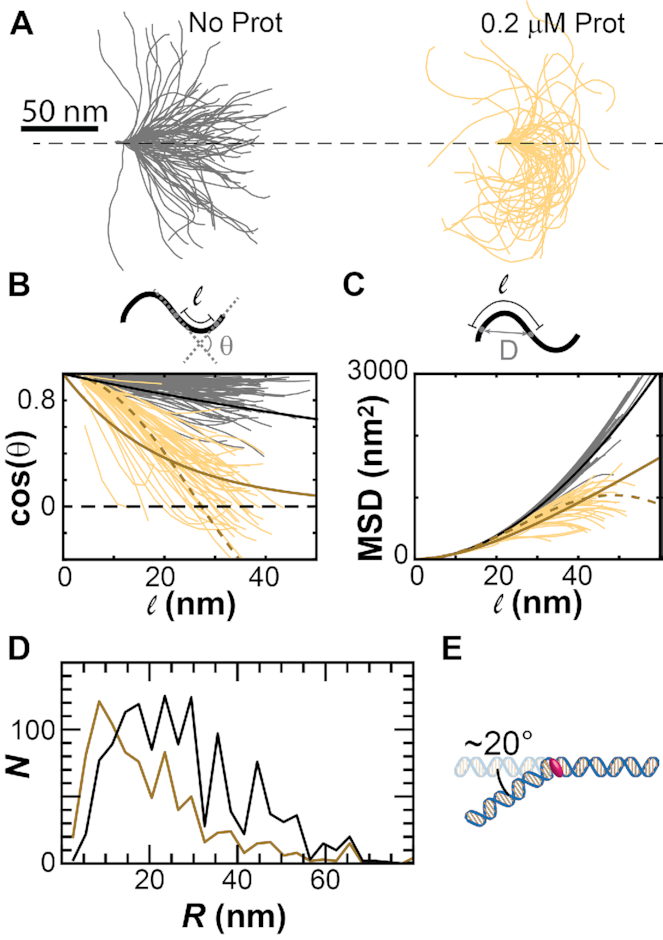
Intermediate folding states have a radius of curvature of ∼10 nm. We compare DNA molecules without protamine (gray) to molecules with 0.2 μM protamine that are folded but not looped (yellow). (A) Contours for the molecules are aligned so that they start at the origin and initially have tangent vectors that point along the x-axis. (B) The cosine of the angle, θ, between segments along the contour decreases with contour length, ℓ. Fits using the model of the flexible polymer (bold, solid lines) approach zero. The fit using the model of the contour bending along a circle (dashed line) crosses over zero and becomes negative. (C) The mean-squared displacement (MSD) calculated from the displacement D for points along the DNA contour as a function of contour length. Fits using the model of the flexible polymer (bold, solid lines) increase with contour length. The fit using the model of the contour bending along a circle (dashed line) decreases at high (>40 nm) contour lengths. (D) Histograms of the radius of curvature for molecules in 0.2 μM protamine that are folded but not looped (dark yellow) and molecules without protamine (black). (E) Cartoon of single protamine creating a 20° bend in the DNA.
