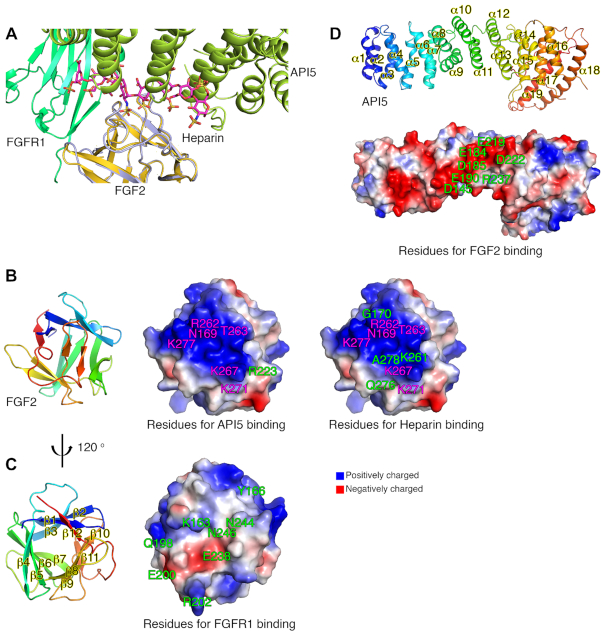
Figure 2.
Structural analysis of the API5–FGF2 complex. (A) Detailed view of the structural superposition of API5–FGF2 on FGF2–FGFR1–heparin (PDB entry 1FQ9) with the FGF2 structure as the central figure. The heparin molecule in the FGF2–FGFR1–heparin complex is colored in magenta and API5 from the API5–FGF2 complex is drawn in limon. FGFR1 is drawn in green. FGF2 in the FGF2–FGFR1–heparin complex is drawn in yellow orange and FGF2 in the API5–FGF2 complex is drawn in light blue. (B) Residues of FGF2 forming hydrogen bonds or salt bridges with API5 or heparin. Residues of FGF2 involved in both API5 and heparin binding are colored in magenta, and residues of FGF2 participating either API5 or heparin interaction are colored in green. (C) Residues of FGF2 forming hydrogen bonds or salt bridges with FGFR1 are colored in green. (D) Residues of API5 forming hydrogen bonds or salt bridges with FGF2. Overall structures of API5 and FGF2 are shown to present the orientation of each molecule. All interface residues of FGF2 with API5, heparin and FGFR1 are summarized in Supplementary Tables S4 and S5.