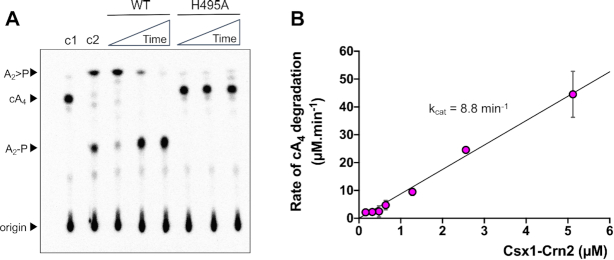
Figure 3.
Csx1–Crn2 rapidly degrades cA4. (A) Phosphorimage of thin-layer chromatography (TLC) visualising degradation of radiolabelled cA4 (∼200 nM) by Csx1-Crn2 or its H495A variant (1 μM dimer) at 50°C over time (1, 10, 60 min). Control reactions incubating radiolabelled cA4 with buffer (c1, negative control) for 60 min or with 1 μM AcrIII-1 for 1 min (c2, positive control) are also shown; the data are representative of three technical replicates. (B) Csx1–Crn2 rapidly degrades cA4 under multiple-turnover conditions. The initial rate of cA4 (256 μM) degradation was quantified at different concentrations of Csx1–Crn2 protein and plotted. A linear function was fitted through the origin and the catalytic rate constant kcat was estimated (kcat = 8.8 ± 0.3 min−1). Each data point is the average of at least three technical replicates and error bars show standard deviation of the mean.