Figure 3.
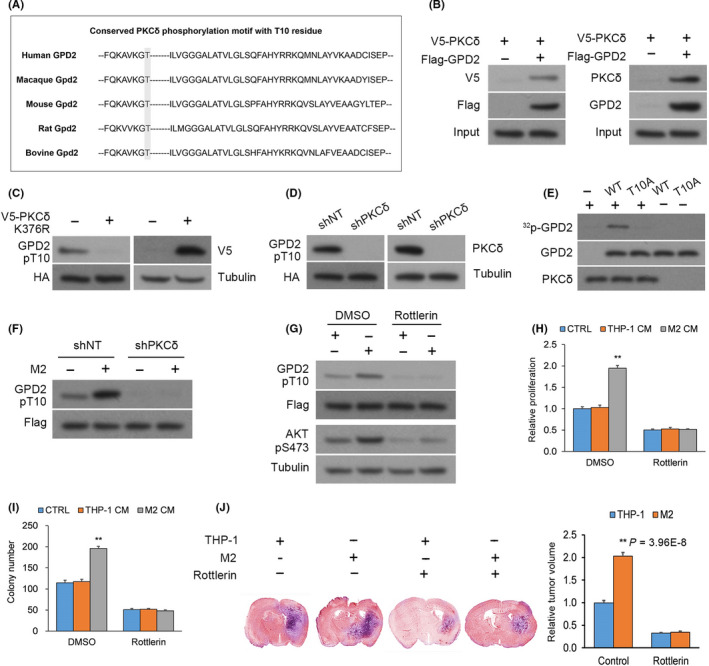
Glycerol‐3‐phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD2) phosphorylation at T10 is mediated by PKCδ. A, The conserved PKCδ phosphorylation motif residing around the T10 residue of GPD2. B, Left panel: Anti–FLAG immunoprecipitation (IP) from U‐87 cultures that underwent co–transfection of V5‐PKCδ with FLAG‐GPD2 or empty plasmid (EP); Right panel: Native anti–GPD2 IP from U‐87 cultures. C, U‐87 cultures with stable transfection of histidine‐biotin (HB)‐GPD2 and transient transfection of kinase‐dead V5‐PKCδ‐KD or EP. D, U‐87 cultures with stable transfection of HB‐GPD2 and lentiviral shPKCδ or scrambled control (shNT). E, In vitro 32P‐labeling assays between recombinant His‐PKCδ (His = His x6 tag) and wild‐type (WT) His‐GPD2‐T10 or mutant His‐GPD2‐T10A. F, U‐87 cells with stable transfection of S‐FLAG‐streptavidin‐binding peptide (SFB)‐GPD2 and lentiviral shPKCδ or shNT co–cultured for 24 h with M2 or THP‐1 cells. G, U‐87 cells with stable transfection of SFB‐GPD2 cultured with/without PKCδ inhibitor rottlerin in M2‐derived or THP‐1‐derived conditioned media (CM). H, Cellular proliferation and (I) colony forming assays in U‐87 cells with stable transfection of SFB‐GPD2 cultured with/without PKCδ inhibitor rottlerin in control media or M2‐derived or THP‐1‐derived CM. n = 3 technical replicates × 3 biological replicates. J, Orthotopic EGFRvIII‐expressing U‐87 gliomas with M2 or THP‐1 cells (1:1) generated in nude mice by intracranial injection. Animals were administered rottlerin or vehicle (n = 9 animals per cohort) and killed 14 d post–implantation; n = 9. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (t test). Means ± standard errors of the mean (SEM). Please refer to Figure S2 for further details
