Figure 1.
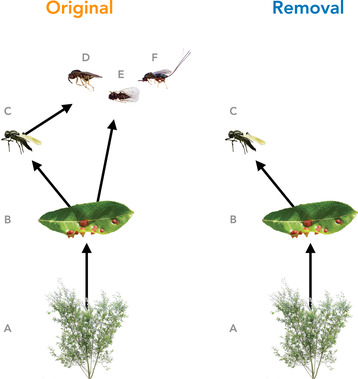
Experimental manipulation of food‐web structure associated with a leaf‐galling midge (B, Iteomyia salicisverruca) feeding on the willow Salix hookeriana (A). Black arrows denote the flow of energy in this network of trophic interactions. In the original food web, we allowed the full suite of egg and larval parasitoids to impose selection. In the removal food web, we used mesh bags to exclude the guild of larval parasitoids, only allowing the egg parasitoid (C, Platygaster sp.) to impose selection. Note that larval parasitoids also impose indirect effects on gall midge fitness through intraguild predation on the egg parasitoid. Larval parasitoids include the following species: Mesopolobus sp. (D, Family: Pteromalidae); Tetrastichus sp. (E, Family: Eulophidae); and Torymus sp. (F, Family: Torymidae).
