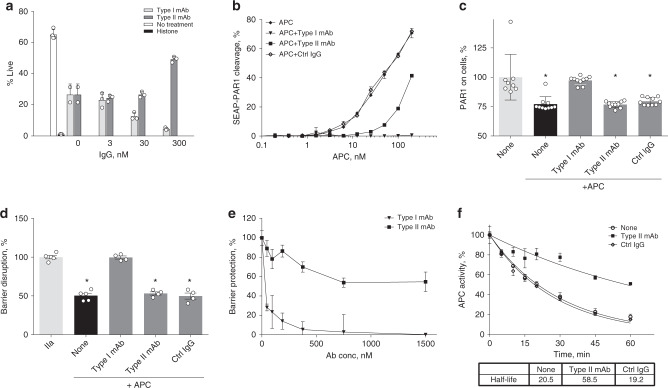
Fig. 4. Distinct effects of type I and type II mAbs on the cytoprotective activities of APC.
a Histone-mediated cytotoxicity assay using HUVECs (% live cells after 2 h). Positive (50 µg/mL histone 3, 0% live cells, black bar) and negative (no histone 3, 70% live cells, open bar) controls. Reduction of histone cytotoxicity by hAPC (20 nM, gray bars) in the presence of type I mAb (light gray) or type II mAb (dark gray). The results are shown as mean + SD of three independent experiments. b Effect of mAbs on PAR1 cleavage of SEAP–PAR1 reporter construct on transfected HEK293/wt-EPCR cells. Shown are mean ± SEM of n = 4 performed on two independent cell seedings. c PAR1 cleavage on EA.hy926 endothelial cells. The ATAP antibody reports PAR1 cleavage at Arg4650. Shown are mean ± SD of N = 10. * denotes p < 0.05 tested with ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test in both (c) and (d). d, e APC (50 nM)-mediated endothelial barrier protection in response to thrombin (2 nM)-induced barrier disruption of an EA.hy926 endothelial cell monolayer was determined using the iCelligence system. d Permeability is expressed as the percentage of maximal barrier disruption induced by thrombin (100%) in the absence of APC. Shown are mean ± SEM of N = 4. e Effect of the mAbs on APC’s barrier protection is expressed as the percentage of the maximal barrier-protective effect of APC in the absence of mAbs. Shown are mean ± SEM of N = 3. f Effect of the type II mAb on the inactivation of APC in human plasma by SERPINs. Data represent mean values ± SD from at least three independent experiments. HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells, SEAP–PAR1 secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) fused to the N terminus of human PAR1, HEK293/wt-EPCR HEK293 cells with stable expression of wild-type human EPCR, SERPINs serine protease inhibitors.