Figure 2. High-altitude SNPs and hypoxia-inducible transcripts are not selectively essential as a function of oxygen levels.
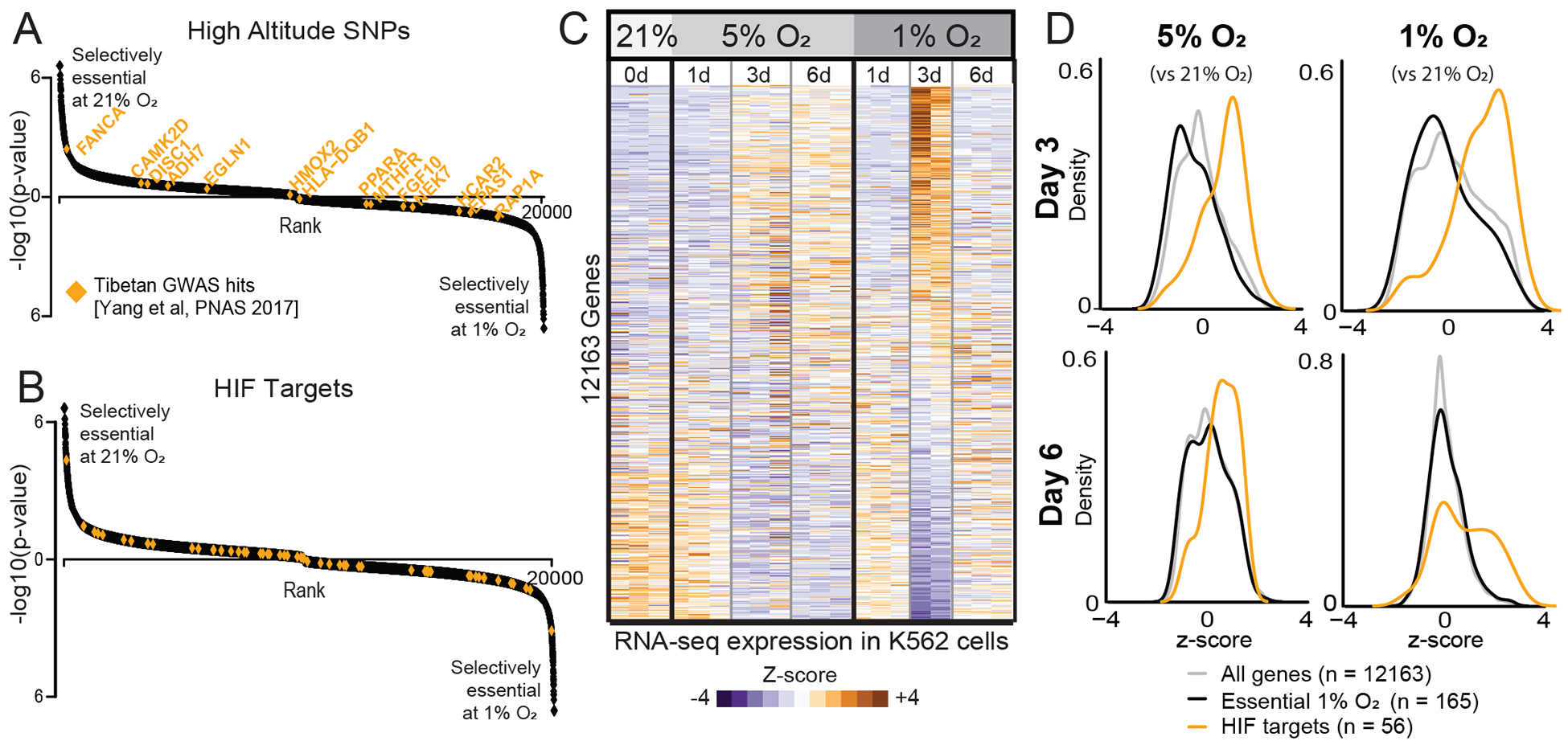
(A) High-altitude SNPs identified in Tibetan high-altitude natives (Yang et al., 2017) shown in orange on genes ranked as in Figure 1D. (B) Canonical HIF targets (Benita et al., 2009) shown in orange. (C) Heatmap of normalized transcript levels in 21%, 5% and 1% O2 performed in triplicate. Relative expression (Z-score) indicates genes down-regulated (blue) or up-regulated (orange) in hypoxia. (D) Distribution of gene expression Z-scores at two time points at 5% and 1% O2 relative to 21% O2. All genes shown in light gray. Genes selectively essential in 1% vs. 21% O2 from CRISPR screen (FDR<0.3) shown in black. Experimentally defined HIF targets (Benita et al., 2009) shown in orange.
