Figure 3. Compositions of the FNC-assembled pDNA/lPEI nanoparticles.
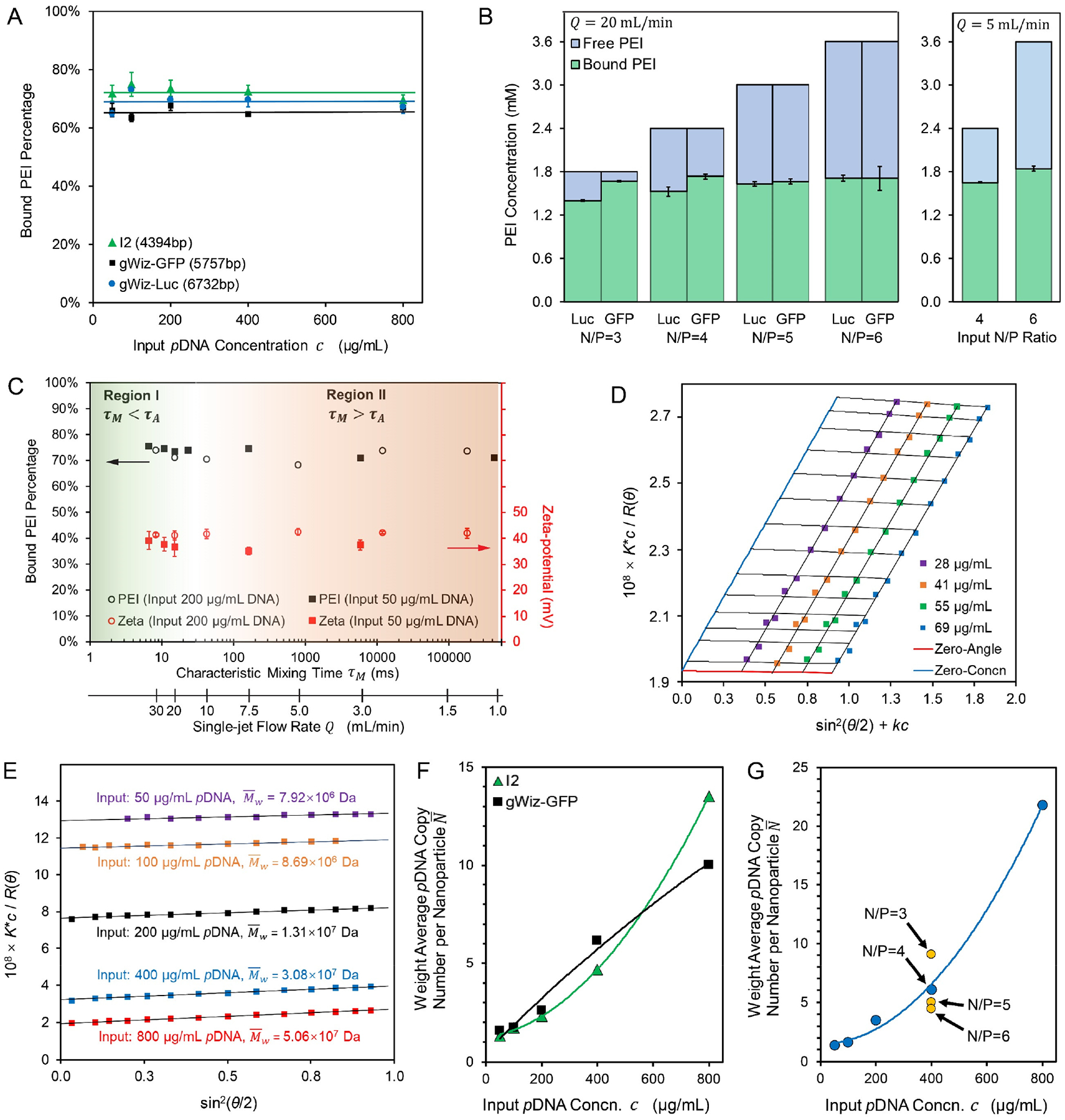
(A) The fraction of bound lPEI and the composition of the assembled nanoparticles remained similar when nanoparticles were prepared at different input pDNA concentrations or with different plasmids; (B) Bound vs. free lPEI amount and proportions with an input N/P ratio from 3 to 6 for gWiz-Luc and gWiz-GFP nanoparticle formulations assembled under a turbulent mixing condition (Q = 20 mL/min, τM = 15 ms < τA) and a laminar mixing condition (Q = 5 mL/min, τM= 790 ms > τA). Labels: Luc and GFP for gWiz-Luc and gWiz-GFP plasmid nanoparticles, respectively; (C) Bound lPEI fraction and zeta-potential of nanoparticles prepared with 50 or 200 μg/mL of gWiz-Luc pDNA under different flow rates, suggesting that all gWiz-Luc/lPEI nanoparticles share the same average composition; (D) A representative Zimm plot for I2/lPEI nanoparticles with a molar mass of 5.32 × 107 Da, also showing the second viral coefficient A approaching zero; (E) Representative Debye plots for gWiz-GFP/lPEI nanoparticles prepared by varying input pDNA concentration for I2 plasmid; (F, G) Calculated weight average pDNA copy numbers per nanoparticle (N) for preparations from lPEI and I2 or gWiz-GFP plasmids at N/P = 4 (F) or gWiz-Luc plasmid at different concentrations and N/P ratios (G).
