FIGURE 1.
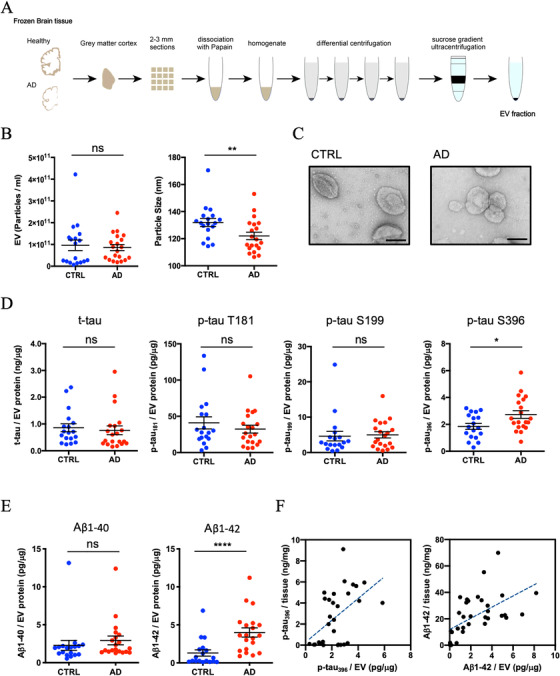
Biophysical and biochemical characterization of extracellular vesicles (EVs) isolated from Alzheimer's disease (AD) and control (CTRL)brain tissues: A, Schematic of extracellular vesicle isolation protocol from human frozen brain tissue (see supporting information for detailed methods). B, Left: particle numbers of brain‐derived EV fraction from control (CTRL) or AD by nanoparticle tracking analysis. P = .6075 by Mann‐Whitney test. Right: Particle size of brain‐derived EV fraction. P = .0095 by Mann‐Whitney test. C, Transmission electron microscopy image of frozen human brain‐derived EVs. Scale bar = 100 nm. Left: CTRL, Right: AD. D, Comparison of total tau and tau phosphorylated at threonine 181, serine 199, and serine 396 in EVs. pS 396 tau; P = .0375 by Mann‐Whitney test. E, Comparison of amyloid beta 1‐40 or 1‐42 in EVs. Aβ1‐42; P < .0001 by Mann‐Whitney test. F, Scattered plot of brain tissue homogenates and brain‐derived EVs. Left: pS396 tau (r = 0.4897, P = .005 using two‐tailed t‐test), Right: Aβ1‐42 (r = 0.5632, P = .0005 using two‐tailed t‐test)
