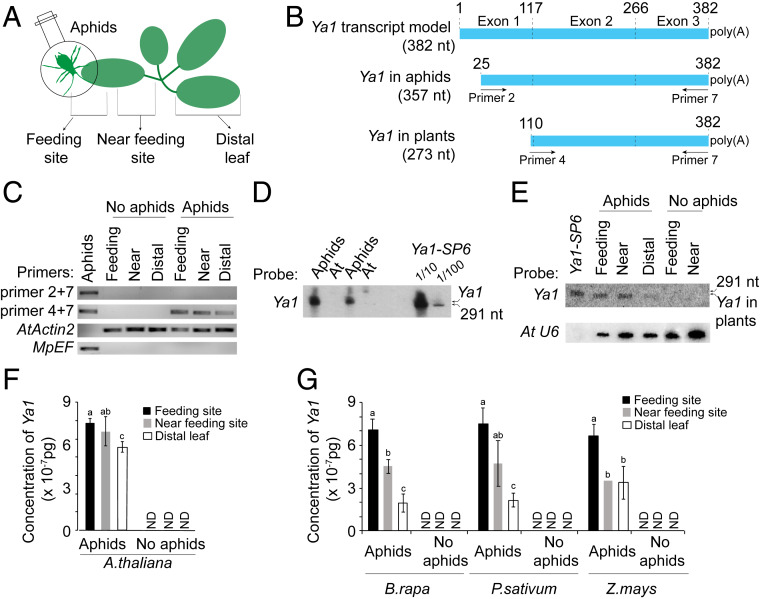
Fig. 4.
The M. persicae Ya1 transcript translocates and migrates to distal leaves in plants. (A) Schematic overview of the experimental setup. The distal leaf was chosen as described in Mousavi et al. (29). (B) Schematic overview of Ya1 transcripts, showing the locations of primers used for amplification in the RT-PCR experiment of C. (C) RT-PCR of Ya1 transcripts in aphids and aphid-exposed A. thaliana Col-0 plants. The 357-nt Ya1 transcript (primers 2 and 7) was found in aphids but not in plants. A 273-nt transcript (primers 4 and 7) was found at aphid feeding sites and was seen to migrate systemically in plants. A. thaliana actin 2 (AtActin2) and M. persicae elongation factor (MpEF) were used to control for the presence of RNA. (D and E) Northern blot hybridizations with a Ya1 probe to detect Ya1 transcript in aphids (D) and plants (E). Arrows at the right of the blots indicate the locations of the in vitro synthesized 291-nt Ya1-SP6 RNA transcript and Ya1 transcript found in aphids and A. thaliana Col-0 plants. Equal RNA loading levels were assessed by stripping blots and subsequent labeling with the A. thaliana U6 probe. (F and G) qRT-PCR to detect systemic migration of M. persicae Ya1 transcript in A. thaliana (F) and B. rapa, P. sativum, and Z. mays (G). The y-axes show Ya1 concentrations based on a standard curve (SI Appendix, Fig. S13). ND, not detected. Bars represent mean ± SD concentrations of Ya1 and two independent biological replicates. Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences between groups (P < 0.01, Student t test).