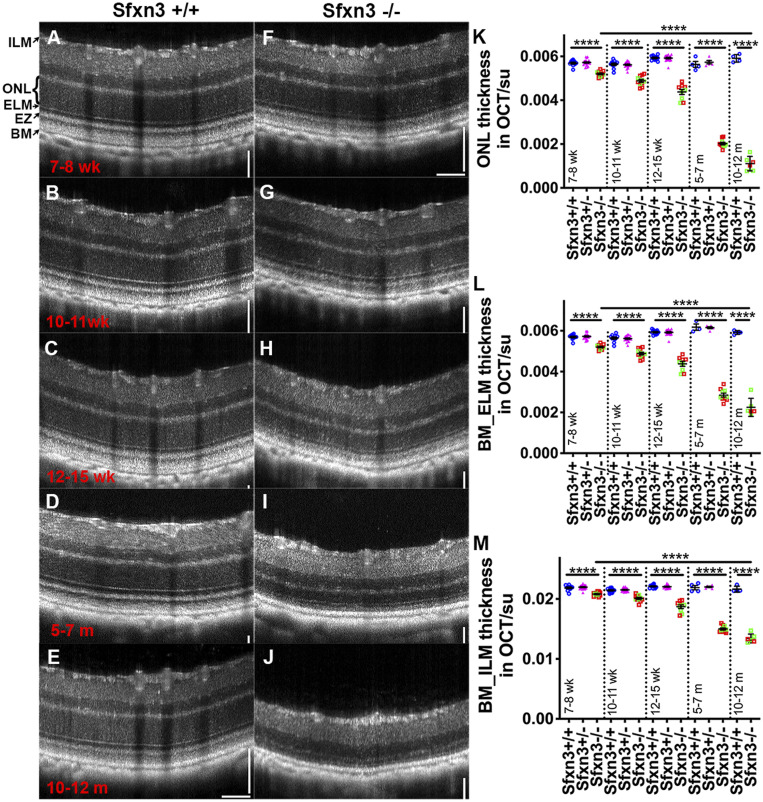
Fig. 4.
OCT images reveal qualitatively and quantitatively abnormal retinal structures in Sfxn3−/− mice. (A–J) OCT images of Sfxn3+/+ and Sfxn3−/− mice were obtained at different ages (7 to 8 wk, 10 to 11 wk, 12 to 15 wk, 5 to 7 mo, and 10 to 12 mo; n = 5 to 11/group/age) to document the progression of retinal deterioration. Hyperreflectivity of the photoreceptor outer segment layer and hyporeflectivity of the interdigitation zone in Sfxn3−/− retinas started as early as 7 to 8 wk of age. There is also progressive thinning of the outer retina. (K–M) For quantitative retinal layer analyses, the following OCT parameters were measured using ImageJ (su, standard units): ONL thickness (K), BM_ELM (L), and BM_ILM (M). Compared with Sfxn3+/+ (blue circles) and Sfxn3+/− (pink triangles) mice, the Sfxn3−/− mice (1-bp insertion in green squares and 4-bp deletion in red squares) demonstrate significant thinning of the retina starting at 7 to 8 wk that worsens progressively with age. There was no difference between the two CRISPR lines. Data points represent individual mice.****P < 0.0001, Student’s t test.