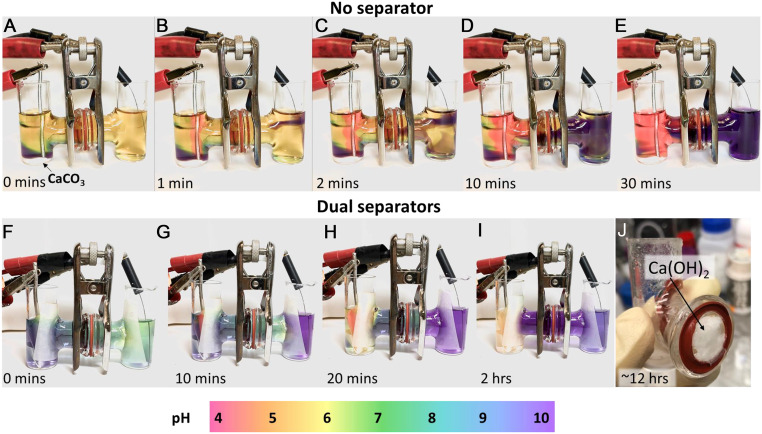
Fig. 3.
Time-lapse images of decarbonation H-cells using platinum electrodes and 1 M NaNO3 in deionized water as electrolyte. Each cell contains a few drops of pH indicator dye, for which the color scale is shown at the bottom. (A–E) Cell containing CaCO3 powder in the anode (left) chamber and with no porous separator between chambers. Electrolysis at 2.5-V cell voltage (∼6-mA current) produces color gradient showing acidic solution at anode (left) and alkaline solution at cathode (right). Close examination of cross-tube shows stratification of the solutions, attributed to density-driven convection. (F–I) Decarbonation cell in which porous fiber separators are used at both chambers to restrict convection, and CaCO3 powder source is contained within a removable cup so that weight loss can be monitored. Note absence of stratification. (J) Ca(OH)2 precipitated in cross-tube after 12 h of electrolysis at a high cell voltage of 9 V to accelerate reaction.