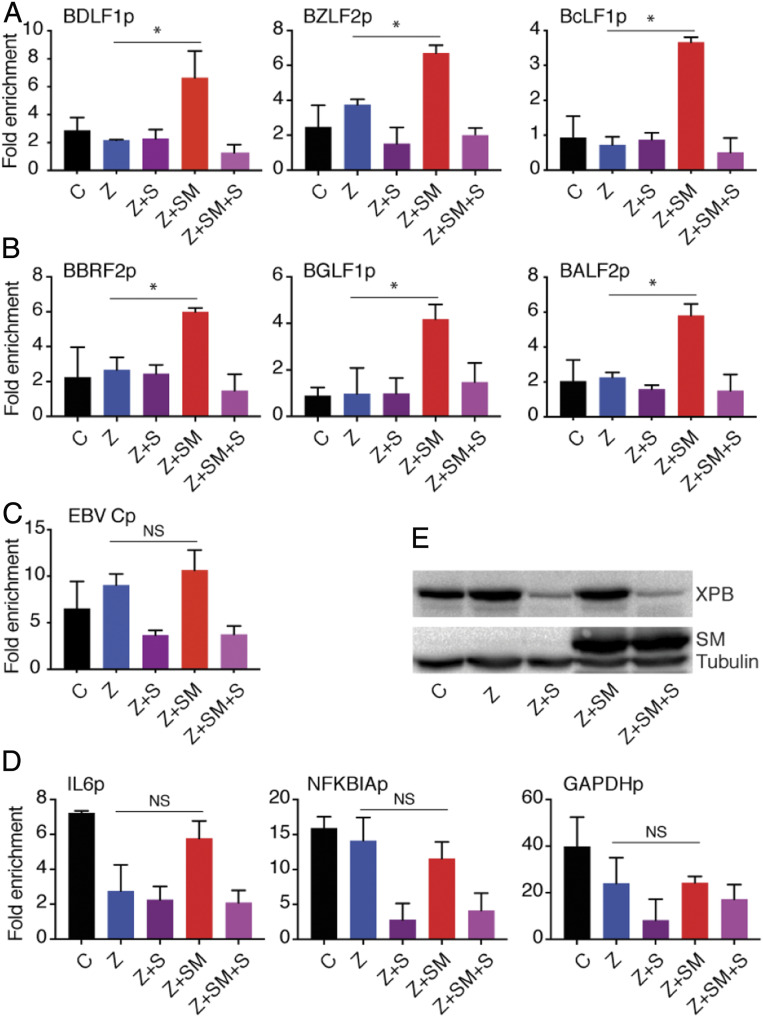
Fig. 5.
EBV SM increases XPB recruitment to EBV lytic promoters but not to cellular promoters or the major EBV latent promoter. ChIP assays to measure effect of SM on XPB binding to EBV lytic promoters during lytic replication. EBV lytic replication in 293 SMKO EBV-infected cells was induced by transfecting with Z plasmid, or with Z and SM plasmids to both induce replication and rescue SM expression. Cells were also transfected with empty vector as an uninduced control. Induced cells were also treated with SPR (+S) or mock-treated with vehicle. Forty-eight hours after lytic induction, proteins were cross-linked to DNA, sheared, and chromatin was immunoprecipitated using an XPB polyclonal antibody. DNA was extracted from IPs and qPCR was performed for several EBV SM-dependent lytic promoters (A), SM-independent lytic promoters (B), the major EBV latency C promoter (C), or cellular promoters (D), to quantitate XPB occupancy during lytic replication. The fold-enrichment over background was calculated using IgG antibody IP as the control in each sample. The error bars indicate the SEM from three different IPs. *P = 0.0004 to 0.03; NS, P = 0.16 to 0.9. (E) Efficacy of XPB depletion by SPR. Western blots was performed from above protein samples and blotted with anti-XPB and anti-SM antibody. The blot was stripped and reprobed with antitubulin as a loading control.