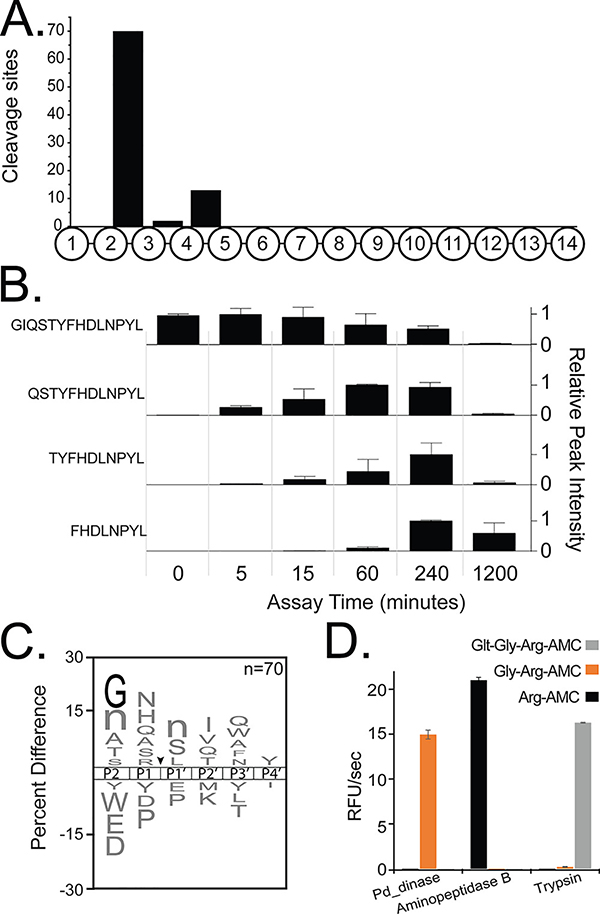
Fig. 1.
Pd_dinase is a sequential di-aminopeptidase. (A) Analysis of cleavage site location within the tetradecapeptide substrate library shows that hydrolysis after 5 minutes incubation generally occurs between the 2nd - 3rd, and 4th - 5th amino acids. (B) A sample peptide from the library showing time-dependent decrease in substrate with concomitant increase in degradation products. (C) An iceLogo plot illustrating the amino acids that are most frequently observed above X-axis and least frequently observed (below X-axis) at the P2 to P4′ positions that surround the cleavage site (black arrow). Glycine at P2 is highlighted in black, as it is the only residue that is significantly enriched (p-value < 0.01), lowercase ‘n’ corresponds to the non-natural amino acid, norleucine. (D) Evaluating Pd_dinase for mono-, di- and tri-aminopeptidase activity. Human aminopeptidase B and trypsin were used as control enzymes for the Arg-AMC and Glt-Gly-Arg-AMC substrates, respectively.