Figure 4. MS4A4A promotes KIT and FcεRI colocalization after co-stimulation of receptors and MS4A4A likely functions in lipid rafts.
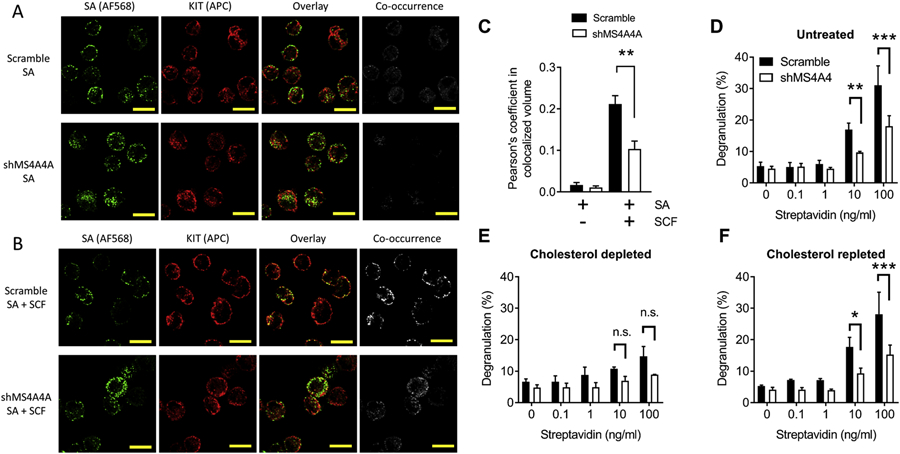
(A-B) Confocal microscopy of human LAD2 MCs show effect of MS4A4A on colocalization of crosslinked FcεRI (green; AF568) and KIT (red; Allophycocyanin) when MCs were stimulated by biotinylated IgE plus AF568 streptavidin (A) compared with stimulation by biotinylated IgE plus AF568 streptavidin in the presence of SCF (B). Top panels show representative images of scramble control treated cells and bottom panels show representative images of shMS4A4A treated cells. (C) Quantification of colocalization assessed by Pearson’s coefficient in colocalized volume above threshold of each stack of high power images. (D) Knockdown of MS4A4A results in reduced degranulation. (E) Depletion of cholesterol with MβCD reduces degranulation and the difference between scramble control and shMS4A4A is no longer significant. (F) Depletion of cholesterol, followed by repletion of cholesterol restores the phenotype to that of untreated cells. Data from D-F are the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ANOVA with Sidak’s posttest.
