Figure 7.
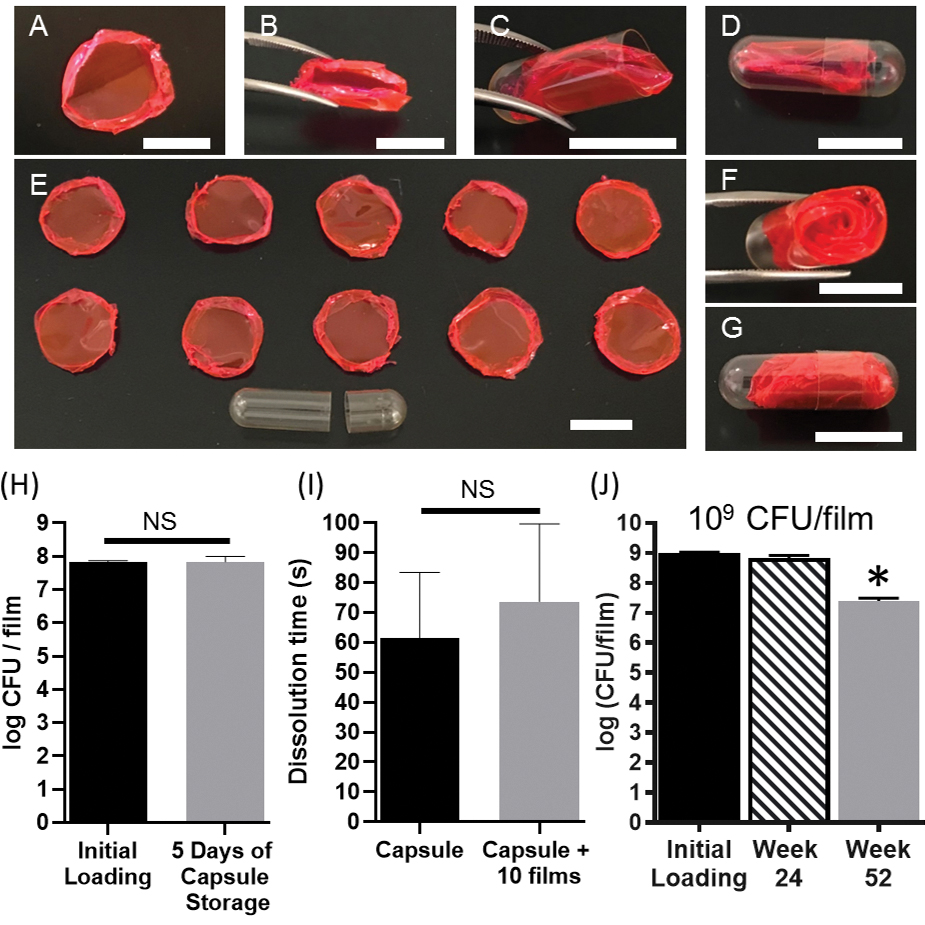
Compatibility of the MBT-film with standard oral capsules. (A) A rhodamine-dyed MBT-film. (B) Folding of the rhodamine-dyed MBT-film. (C) Insertion and (D) capping of the rhodamine-dyed MBT-film into a 00-sized oral capsule. (E) Ten rhodamine-dyed MBT-films and an empty 00-sized capsule. (F) Insertion and (G) capping of ten rhodamine-dyed MBT-films into a 00-sized capsule. Scale bars = 1 cm. (H) Storage of MBT films (3%PVA+MRS+glycerol with 108 L. casei ATCC393) in 00-sized capsules. (I) Capsule dissolution time with or without film inclusion. (J) Storage of L. casei ATCC393 in 3%PVA+MRS+glycerol at 4°C at 109 CFU film−1 loading. Each error bar represents standard deviation (n = 3). (H-I) Statistical analysis was conducted using Student’s t-test (statistical significance defined at p < 0.05). NS: not significant. (J) Statistical analysis was conducted using one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Dunnett’s test (statistical significance defined at p < 0.05). *: significantly different from initial loading.
