Figure 4. New Discovery with Old Drugs.
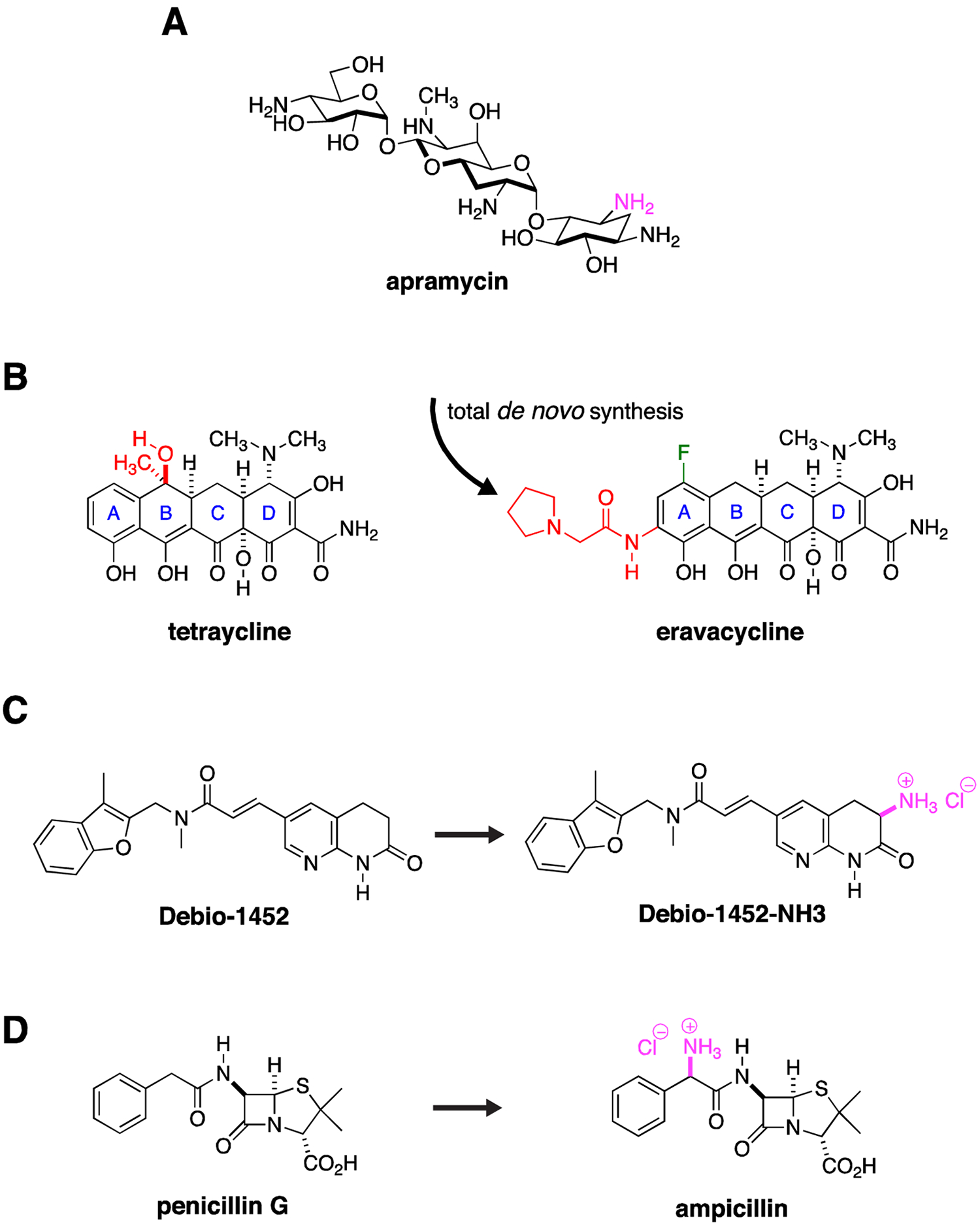
(A) Apramycin has activity against CRE. One amino group (purple) is modified by a circulating AAC(3)-IV acetylase. Derivatization around this site may significantly extend its activity spectrum by blocking acetylase activity. (B) Total de novo synthetic approaches allow exploration of a range of structural permutations not possible with semi-synthesis approaches that modify an existing natural product. The total synthesis of eravacycline allowed installation of a fluorine (green) and an pyrrolidinylacetylamino substituent (red) on the tetraycline A ring while removing methyl and hydroxy groups (red) on the tetraycline B ring, derivatization that would not have been possible by modification of the existing tetracycline scaffold. (C) The Gram-positive, FabI inhibitory activity of Debio-1452 was extended to Gram-negative pathogens through installation of a primary amine (purple), one of the so called eNTRyway rules that are associated with Gram-negative envelope penetration. (D) Similarly, the selective Gram-positive activity of penicillin G was extended to Gram-negative pathogens through installation of a primary amine (purple) to create ampicillin.
