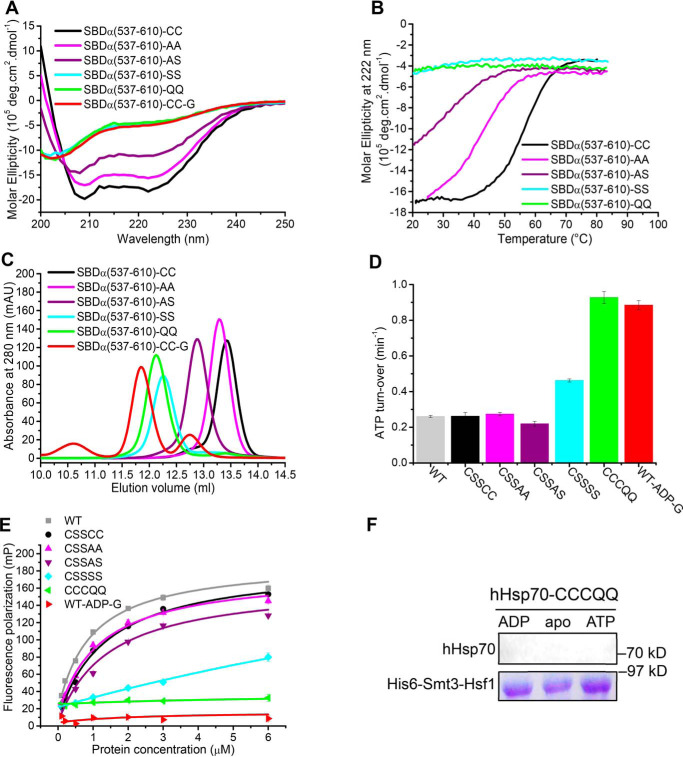
Figure 8.
Mutation or glutathionylation within the SBDα lid of hHsp70 alters the activity of hHsp70 through reducing the stability of the α-helical structure. A–C, conformation and secondary structure of untreated hHsp70 SBDα(537–610) (-CC, black), SBDα(537–610)-AA (-AA, magenta), SBDα(537–610)-AS (-AS, purple), SBDα(537–610)-SS (-SS, cyan), SBDα(537–610)-QQ (-QQ, green), and glutathionylated SBDα(537–610) (-G, red) were compared by far-UV CD (A), thermal denaturation monitored by the CD signal at 222 nm (B), and SEC (C). D and E, activity of full-length WT and mutant hHsp70 was compared by ATPase activity measured with a malachite green assay (D) and peptide binding measured with fluorescence polarization (E); untreated WT hHsp70 (WT-CC, gray), untreated hHsp70-CSSCC (-CC, black), hHsp70-CSSAA (-AA, magenta), hHsp70-CSSAS (-AS, purple), hHsp70-CSSSS (-SS, cyan), hHsp70-CCCQQ (-QQ, green), and glutathionylated WT hHsp70 in the presence of 0.5 mm ADP (WT-ADP-G, red). The data shown are the mean of three independent measurements (each of three replicates), and the error bars represent S.E. F, interaction of hHsp70-CCCQQ in the absence or in the presence of 1 mm ADP or ATP with Hsf1 was detected by a pulldown assay, performed as in Fig. 6E.