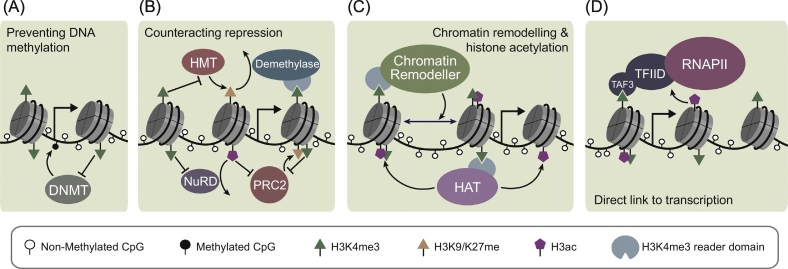
Fig. 4.
The relationship between H3K4me3 and transcriptionally permissive chromatin.
(A) H3K4me3 has been proposed to counteract methylation of CpG islands by preventing both binding and activation of the de novo DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs). The position of the transcription start site is illustrated as an arrow in each panel and a legend for the chromatin modifications is shown below the panels.
(B) H3K4me3 counteracts acquisition of repressive chromatin modifications by preventing binding of histone methyltransferases (HMTs) while promoting removal of repressive methylation by stabilising binding of demethylases. In addition to inhibiting its catalytic activity, H3K4me3 may also inhibit PRC2 by preventing binding of NuRD and hence indirectly reduce PRC2 association with chromatin.
(C) Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and chromatin remodellers bind to H3K4me3 and contribute to an accessible and transcriptionally permissive chromatin architecture at CGI-associated gene promoters.
(D) The TAF3 subunit of TFIID binds H3K4me3 and promotes pre-initiation complex formation, providing a direct link to transcription. This interaction is enhanced by histone acetylation.