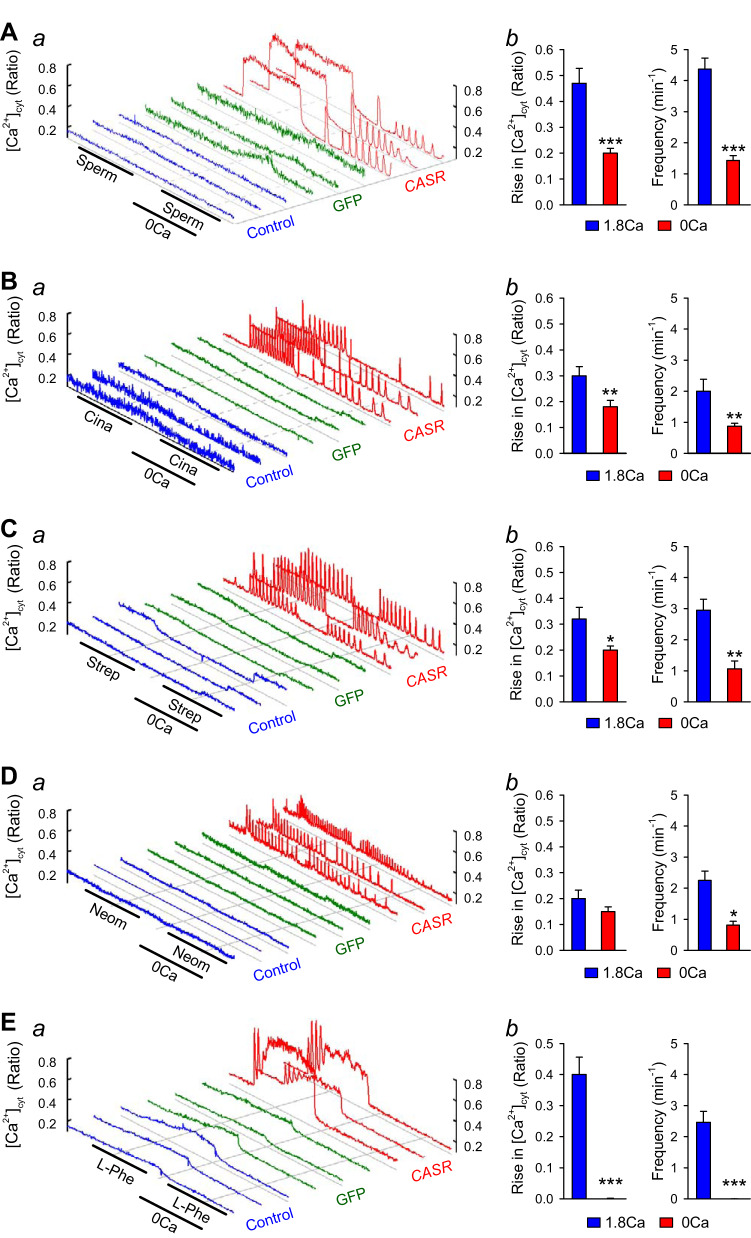
Fig. 2.
Characterization of spermine-, cinacalcet-, streptomycin-, neomycin-, and l-phenylalanyl-induced cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]cyt) increase in calcium-sensing receptor (CASR)-transfected human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cells. Representative traces (a) showing changes in [Ca2+]cyt in control (left 3 curves), green fluorescent protein (GFP)-transfected (middle 3 curves), and CASR-transfected (right 3 curves) HEK293 cells before, during, and after extracellular sequentially application of 3 mM spermine (A), 1 μM cinacalcet (B), 100 μM streptomycin (C), 100 μM neomycin (D), and 3 mM l-phenylalanyl (E) in the presence or absence (0 Ca) of 1.8 mM extracellular Ca2+. Summarized data (means ± SE; b) showing the amplitude and frequency of spermine- (A), cinacalcet- (B), streptomycin- (C), neomycin- (D) and l-phenylalanyl-induced (E) increases in [Ca2+]cyt in presence or absence of 1.8 mM extracellular Ca2+ in HEK293 cells transfected with CASR constructs; n = 5 for each group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 vs. 1.8Ca2+ (Student’s t test).