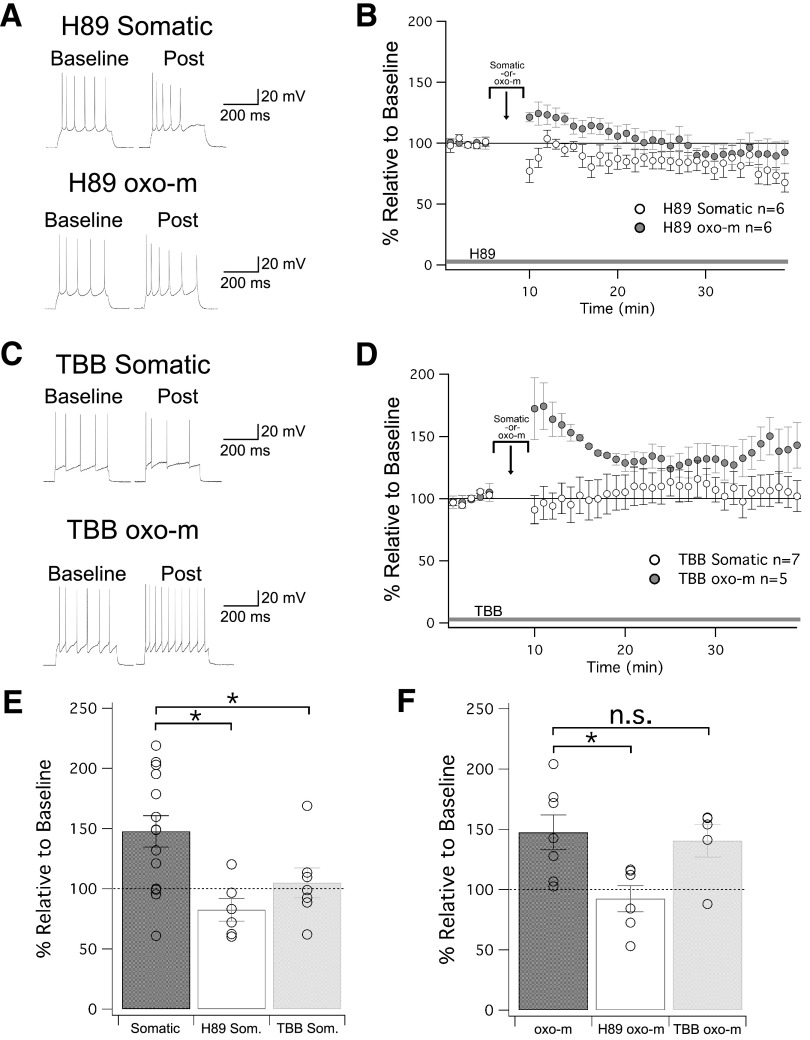
Figure 4.
The role of PKA and CK2 in regulating SK2 channels in intrinsic plasticity. A, Example traces for cells treated with H89, a PKA inhibitor that was present in the bath for the duration of the experiment. B, Time graph for changes in spiking relative to baseline. Either somatic depolarization or oxo-m was applied from minute 5 to 10. C, Example traces for cells treated with TBB, a CK2 inhibitor that was present in the bath for the duration of the experiment. D, Time graph for changes in spiking relative to baseline. Either somatic depolarization or oxo-m was applied from minute 5 to 10. E, Bar graph for depolarization-induced changes in spiking relative to baseline. Both H89 and TBB bath application prevented intrinsic plasticity. F, Bar graph for oxo-m-induced changes in spiking relative to baseline. H89, but not TBB, prevented intrinsic plasticity; *p < 0.05. n.s. = nonsignificant.