Table 2.
Cascade Optimization with Methyl Acrylate
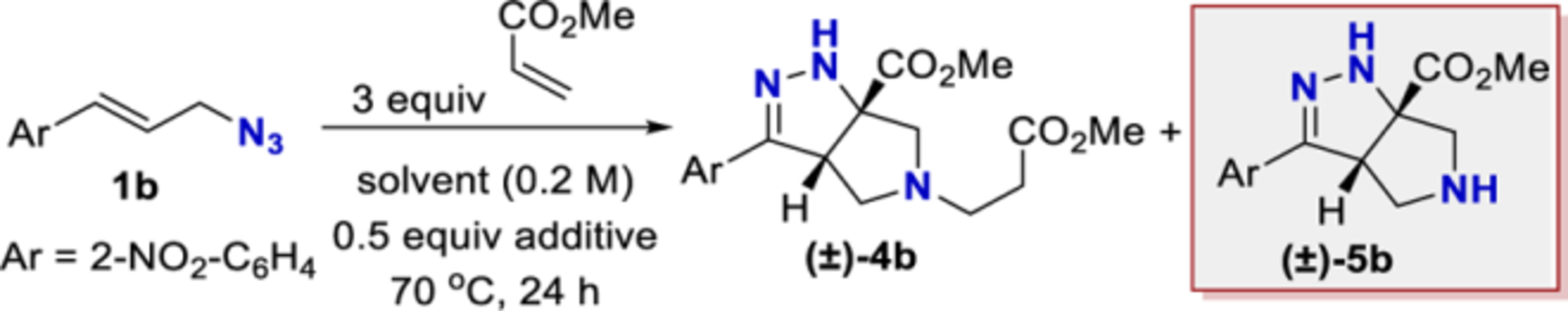 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | solvent | additive | % 2ba | % 4ba | % 5ba |
| 1 | DMSO | nd | 14 | 77 | |
| 2 | MeOH | nd | 95 | n.d. | |
| 3 | hexane | nd | 54 | 35 | |
| 4 | THF | 34 | nd | 46 | |
| 5 | C6H6 | 37 | nd | 11 | |
| 6 | C6H6 | AcOH | nd | 67 | nd |
| 7 | C6H6 | HFIP | nd | 55 | 17 |
| 8 | C6H6 | DMAP | nd | 8 | 80 |
| 9 | C6H6 | pyridine | 5 | nd | 41 |
| 10 | C6H6 | TEA | nd | nd | 85 |
| 11 | C6H6 | DIPEA | nd | nd | 91 |
| 12 | PhMe | DIPEA | nd | nd | 83 |
| 13 | THF | TEA | nd | nd | 72 |
| 14 | THF | DIPEA | nd | nd | 78 |
Reactions were conducted with azide 1b (70 μmol), methyl acrylate (210 μmol), and an additive (35 μmol) in solvent (0.2 M) at 70 °C. Conversion and yield were determined by calibrated GC-FID analysis. Reactions were run in duplicate, and the average value is reported. Not detected = nd.
