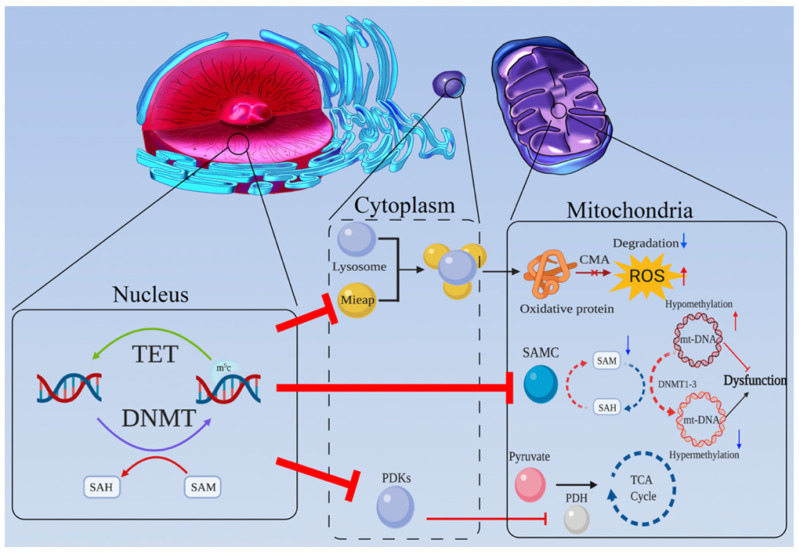
Figure 2.
Mitochondrial dysfunction caused by DNA methylation is a potential trigger for aerobic glycolysis. (a) MtDNA is crucial for mitochondrial function. Once mtDNA is methylated by mt-DNMTs, OXPHOS is inhibited. Due to promoter hypermethylation, SAMC is downregulated, and mitochondrial SAM levels decrease. Hence, the methylation status of mtDNA may be downregulated. (b) Mieap-mediated, lysosomal involved oxidative protein clearance is an important pathway for the maintenance of normal mitochondrial function. Hypermethylation of Mieap causes mitochondria to become severely dysfunctional. (c) The activity of PDH can be inhibited by PDKs, which are modulated by DNA methylation.