Figure 2. Knockdown screen targeting kinases from the MIB-MS HGSOC tumor signature identifies MRCKA as a candidate therapeutic target.
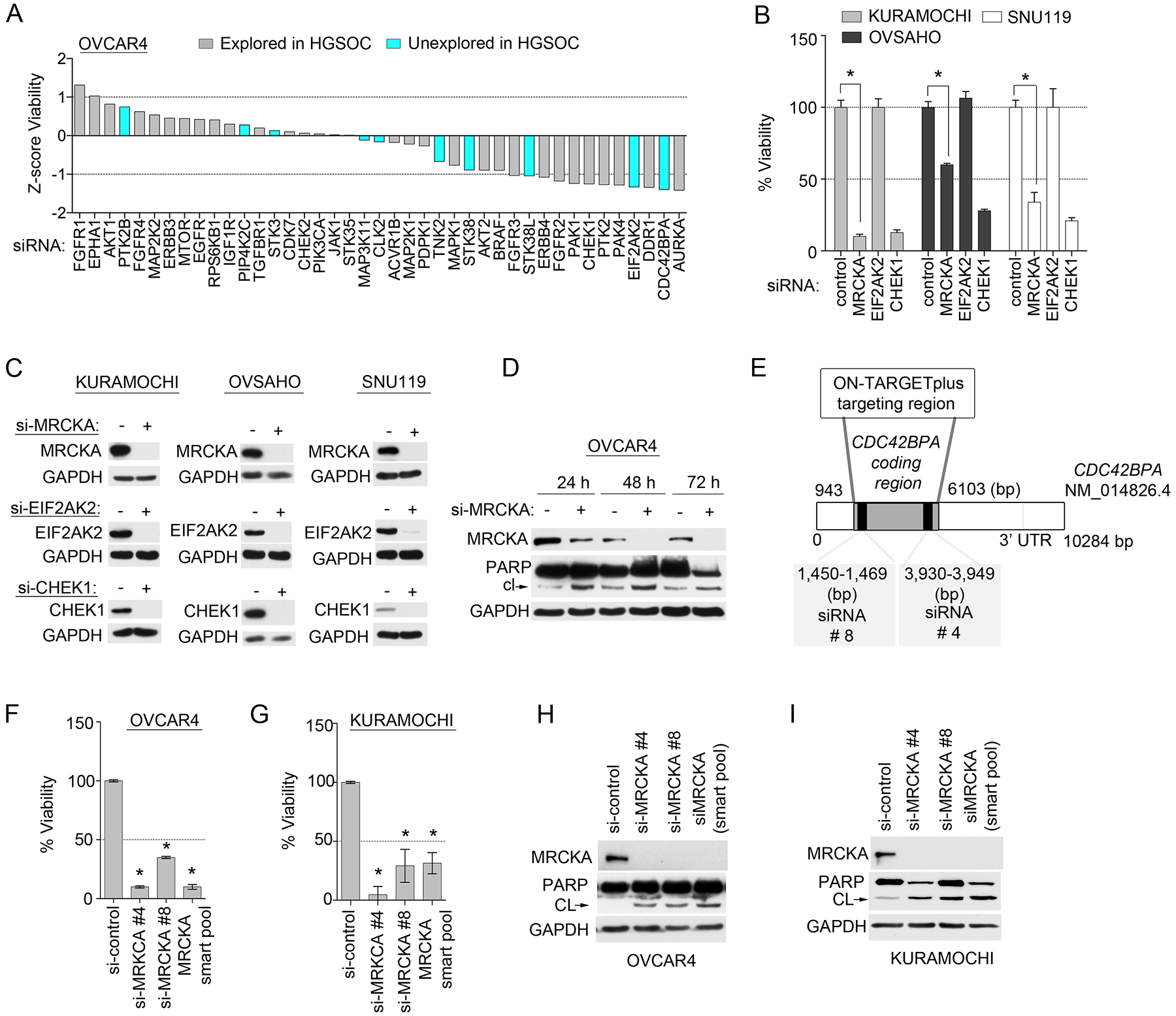
(A) Cell-Titer Glo assay for cell viability of established HGSOC cell line transfected with siRNAs targeting the indicated kinases or with control siRNA (NT2) and cultured for 120 hours. Data were analyzed as Z-scores; presented as means of 3 independent assays. (B) Cell viability in 3 additional established HGSOC cell lines to those presented in (A), cultured and assessed after knockdown of select kinases as described in (A). Data were analyzed as % cell viability; presented as means ± SD of 3 independent assays. *P≤0.05 by Student’s t-test. (C) Knockdown efficiency of MRCKA, EIF2AK2 and CHEK1 in HGSOC cell lines presented in (B). Cells were transfected with siRNAs targeting MRCKA, EIF2AK2, CHEK1/2 or with control siRNAs and cultured for 72 hours. MRCKA and cleaved PARP protein abundance was assessed by immunoblot every 24 hours. Blots are representative of 3 independent experiments. (D) Apoptosis assessed by immunoblotting for cleaved-PARP abundance in OVCAR4 cells. Cells were transfected with siRNAs targeting MRCKA or with control siRNAs and cultured for 72 hours. MRCKA and cleaved PARP protein abundance was assessed by immunoblot every 24 hours. Blots are representative of 3 independent experiments. (E) Targeted spectrum in CDC42BPA-coding gene of 2 distinct siRNAs used in study. CDC42BPA siRNAs 1 and 2 are present in the siGENOME pools. (F to I) Effect of MRCKA knockdown with 2 distinct siRNAs on cell viability by Cell-Titer Glo assay and apoptosis by cleaved-PARP immunoblotting in OVCAR4 (F and H) and KURAMOCHI (G and I) cells transfected with CDC42BPA-targeted siRNAs for 48 hours. Data are means ± SD of 3 independent experiments. *P≤0.05 by Student’s t-test.
