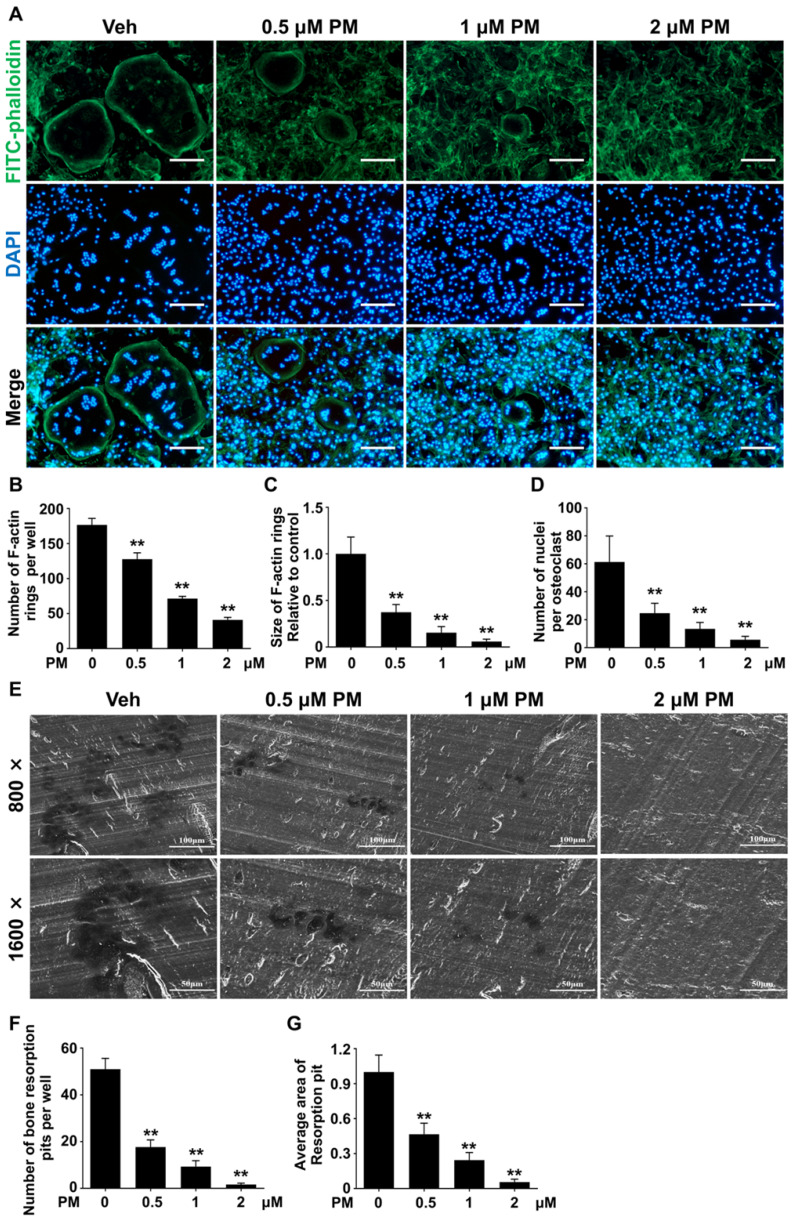
Figure 7.
Pharmacological activation of Hh signaling by PM inhibited RANKL-induced F-actin ring formation and osteoclastic bone resorption in vitro. (A) Representative images of phalloidin staining of BMM clutures treated with RANKL for 6 days in the presence of 0, 0.5, 1, or 2 μM PM. F-actin rings. Green, F-actin; Blue, nuclei. Scale bar, 200 μm. (B-D) Quantitative analyses of F-actin rings showing number of F-actin rings per well (B), relative size of F-actin rings (C), and number of nuclei per osteoclast (D) in BMM clutures treated with RANKL for 6 days in the presence of 0, 0.5, 1, or 2 μM PM. (E) Representative scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of resorption pits on bovine slices seeded with differentiating osteoclasts in the presence of 0, 0.5, 1, or 2 μM PM. (F-G) Quantification of number (F) and average area (G) of bone resorption pits on SEM images. All values were calculated from three independent replicates, and presented as mean ± SD. ** indicated P<0.01, compared with vehicle-treated group.