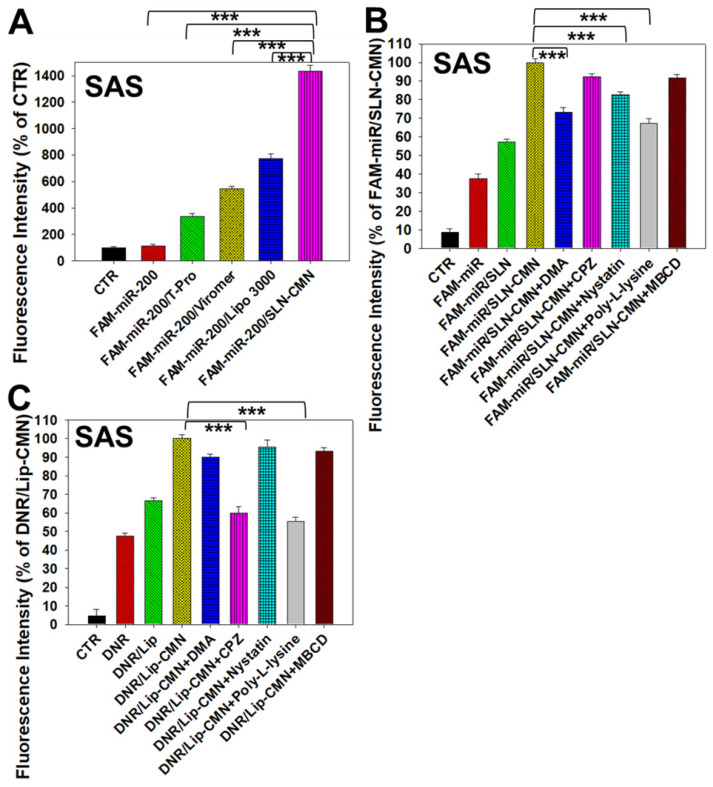
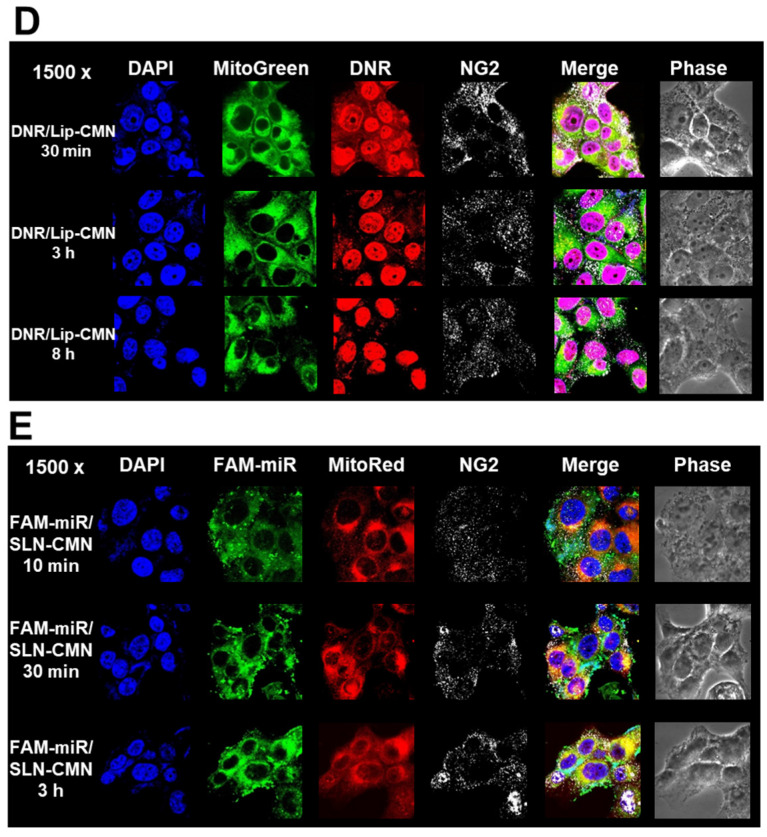
Figure 3.
Transfection, cellular internalization, and intracellular trafficking of various miR-200 formulations in SAS cells. (A) Flow cytometry of the transfection efficiency (%) of FAM-miR-200 in the presence of different transfection reagents for 24 h. FAM-miR-200/Lipo 3000: FAM-miR-200/Lipofectamine 3000. (B) Endocytosis mechanisms of FAM-miR-200/SLN-CMN in SAS cells were detected by incubating the cells with specific endocytosis inhibitors at 37 °C for 1 h. Then, the cells were treated with FAM-miR formulations for another 3 h. The endocytosis inhibitors included 5-(N,N-dimethyl) amiloride (DMA), nystatin, chlopromazine (CPZ), poly-L-lysine, and methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MBCD). ***P < 0.001 compared with FAM-miR-200/SLN-CMN without the inhibitor. (C) After treatment with the above endocytosis inhibitors for 1 h at 37 °C, the cells were treated with different DNR formulations for another 3 h. ***P < 0.001 compared with DNR/Lip-CMN without the inhibitor. (D) DNR/Lip-CMN was added to the cells for 30 min, 3 h, and 8 h. Intracellular localization in SAS cells was observed through CLSM. Blue: DAPI (a nuclear dye); green: MitoGreen (MitoTracker Green; a mitochondrial dye); red: DNR; Gray: NG2 (nerve/glial antigen 2). (E) FAM-miR-200/SLN-CMN was added to the cells for 10 min, 30 min, and 3 h. Intracellular trafficking was observed by CLSM in SAS cells. Blue: DAPI; green: FAM-miR200; red: MitoRed (MitoTracker Red; a mitochondrial dye); gray: NG2.