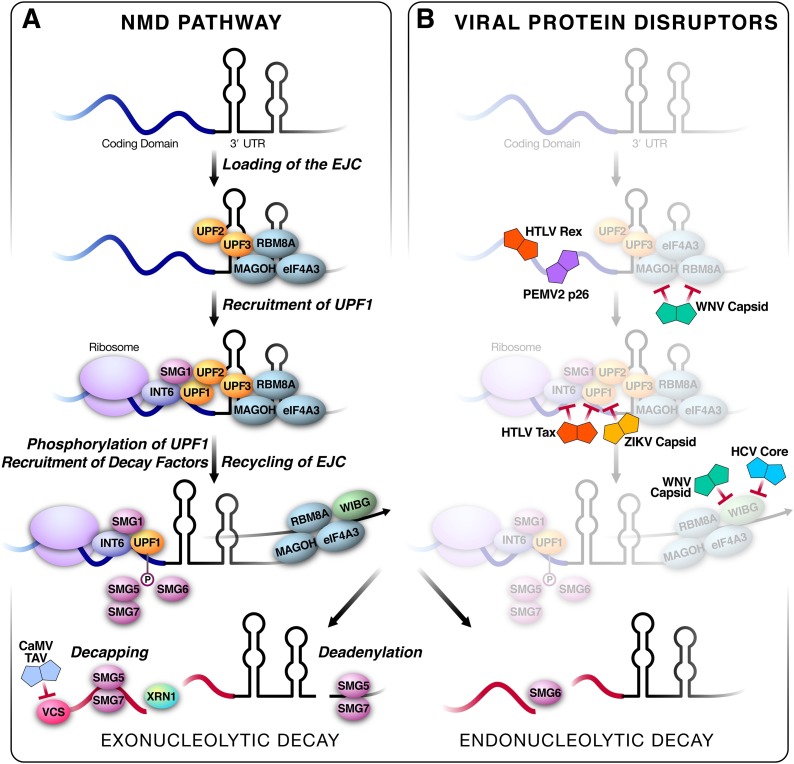
Fig. 1.
A) Schematic of the NMD pathway: Initially, a spliced mRNA has the exon junction complex (EJC) loaded on to the mRNA. This includes the core members: RBM8A, eIF4A3, and MAGOH. When there is a PTC upstream of a retained EJC, UPF2 and UPF3 act as a bridge to recruit the UPF1/SMG1 complex and initiate the NMD pathway. UPF1 is then phosphorylated by SMG1, leading to the recruitment of the decapping and deadenylating complex created by SMG5/SMG7, resulting in exonucleolytic decay. SMG6 is recruited for a separate endonucleolytic decay pathway. In plants, the complex VARICOSE (VCS) is responsible for decapping mRNAs. B) Viral interactors overlaid on the NMD pathway: HTLV Rex and PEMVp62 protects mRNA from degradation by blocking NMD initiation on transcripts. WNV capsid interacts and interferes with RBM8A and MAGOH. HTLV Tax interferes with INT6 and UPF1 function, whereas ZIKV capsid blocks UPF1 function. WNV capsid and HCV core interfere with WIBG recycling of EJC factors. The CaMV TAV protein blocks decapping by interfering with the complex VCS.