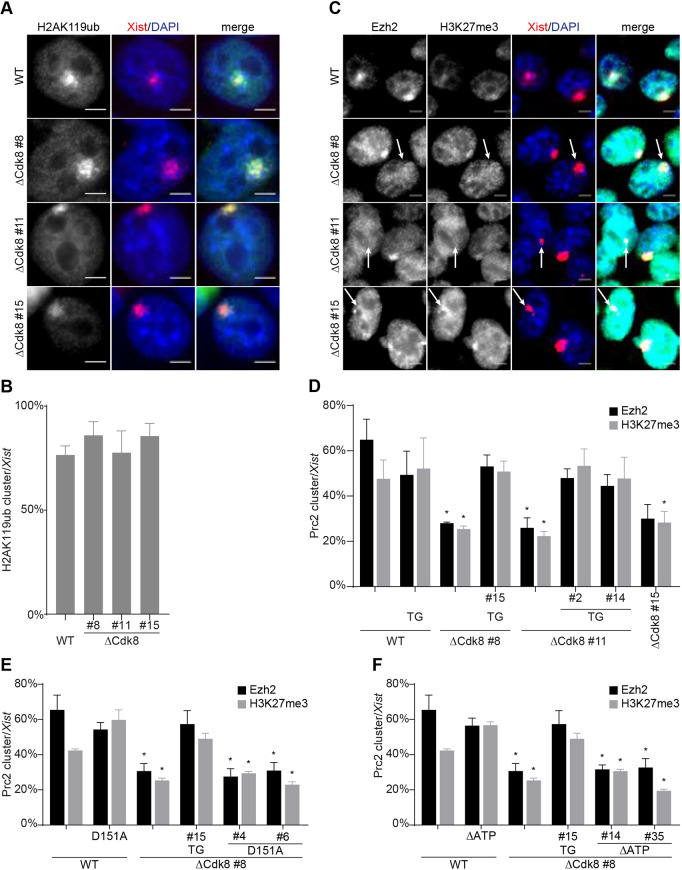
Fig. 3.
Cdk8 is required for efficient PRC2 recruitment by Xist. (A) Images of combined H2AK119ub immunofluorescence with Xist RNA FISH (red) for wild-type and ΔCdk8 cells. DAPI was used to stain DNA (blue). (B) Quantification of the percentage of Xist clusters with H2AK119ub foci after 24 h of Xist expression in ΔCdk8 and wild-type ESCs. Percentages are relative to counted Xist clusters; experiments were performed in triplicate; data are mean±s.d. (C) Combined immunofluorescence (Ezh2 and H3K27me3) with Xist-FISH (red) for wild-type and ΔCdk8 ESCs. White arrows indicate Xist clusters lacking PRC2 marks. DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). (D-F) Quantification of the percentage of Xist clusters with PRC2 (Ezh2 and H3K27me3) foci after 24 h of Xist expression in (D) ΔCdk8 ESCs and wild-type Cdk8 transgene complemented ΔCdk8 ESCs, (E) D151A and (F) ΔATP mutant Cdk8 transgene complemented ΔCdk8 ESCs. Percentages are relative to counted Xist clusters. Wild-type, ΔCdk8 #8 and ΔCdk8 #8 TG#15 samples are the same in E and F. The experiments were performed in triplicate. Data are mean±s.d.; asterisk indicates significant changes relative to WT (P<0.05). Scale bars: 5 μm.