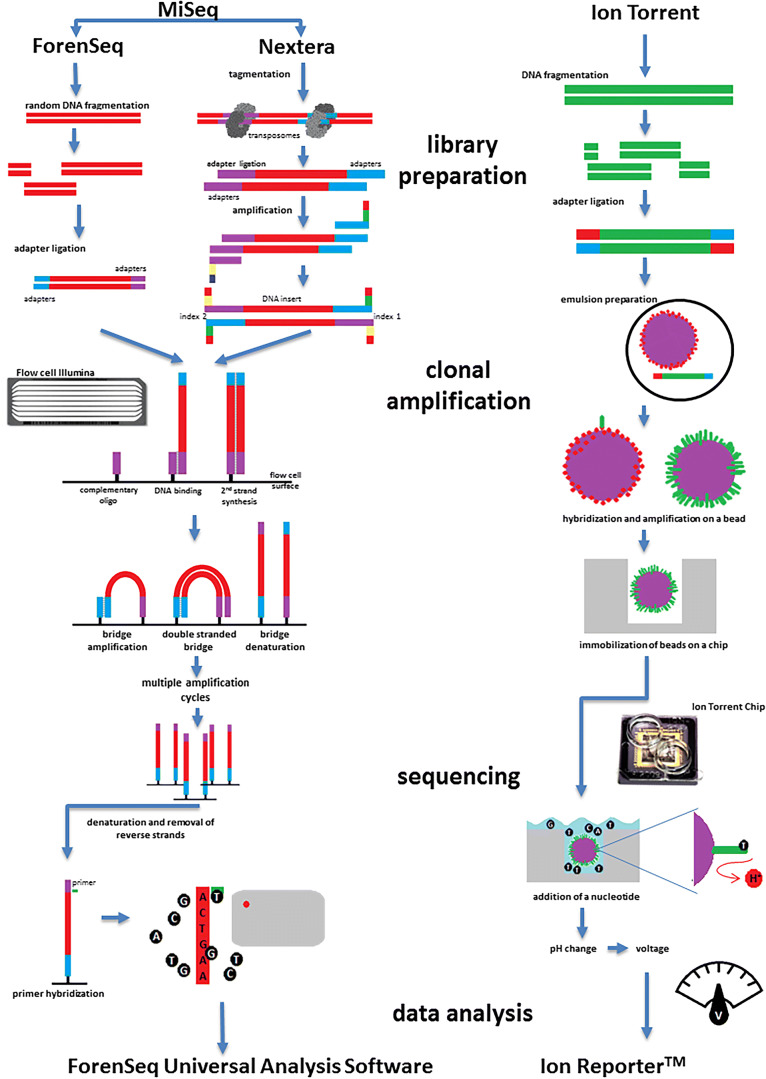
Fig. 2.
Schematic illustration of sequencing with MiSeq FGx and Ion Torrent, a MiSeq: Forenseq is a library prep used for STR and SNP sequencing (autosomal STRs, sex, geographical ancestry, and phenotypic SNPs); alternatively, Nextera is utilized for mtDNA sequencing. In the process of sample preparation, adaptors are added to DNA fragments in a two-step PCR reaction in order to enable DNA binding to a glass slide. In the next step, the fragments are clonally amplified on the slide and sequenced. The template strand is extended with one nucleotide at a time. The reaction of polymerization is halted due to the use of 3′-O-azidomethyl-dNTPs that are fluorescently labeled. The base incorporation is followed by removal of unincorporated bases and imaging using CCD camera. Subsequently, the 3′ block and the fluorescent tag on the incorporated nucleotide are removed and the reaction proceeds to the next cycle. b Ion Torrent: sample preparation of DNA fragments for sequencing on Ion Torrent is similar to the workflow utilized by Roche 454 sequencer, followed by amplification of adaptor-ligated DNA hybridized to beads using emulsion PCR (Margulies et al. 2005) [1]. The beads are distributed to microwells, where sequencing by synthesis occurs. The sensor located at the bottom of the well converts the changes in pH into a voltage signal proportional to the number of incorporated bases