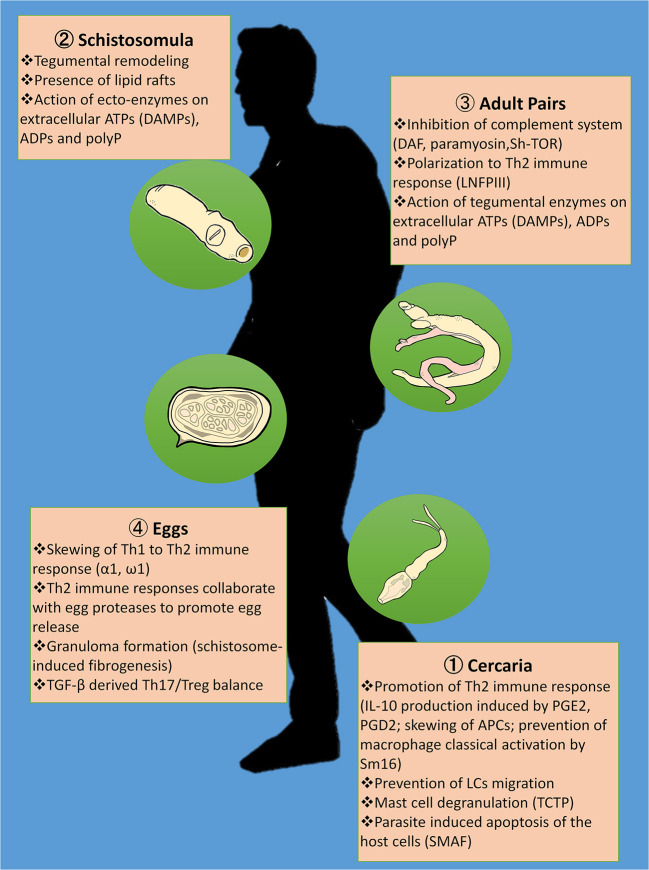
Figure 1.
Summary of proposed immunomodulatory strategies of the schistosome in evading the host immune responses. Skewing of Th1 to Th2 immune response is very much evident during cercarial penetration through IL-10 production induced by prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and prostaglandin D2 (PGD2), prevention of macrophage classical activation by Sm16 and disorientation of the antigen presenting cells (APCs); lodging of the adult schistosome pairs in the veins through the interactions between lacto-N-fucopentose III (LNFPIII) and toll like receptors (TLRs); and egg deposition in the intestinal and liver tissues through the immunomodulatory effects of the egg's excretory-secretory proteins (ES) to CD4+ effector responses including α1 and ω1. In addition, the cercariae are able to evade innate immunity in the skin by preventing migration of Langerhans cells (LCs), mast cell degranulation promoted by the translationally-controlled tumor protein (TCTP) homolog in schistosomes, and Schistosoma mansoni apoptosis-inducing factor (SMAF)-mediated host cell death. Schistosomula's tegumental remodeling and the presence of lipid rafts covering the parasite render them undetectable to immune responses during migration. Once the adult schistosomes settle in the mesenteric veins, they become capable of evading the host complement system through the abstraction of erythrocytes' decay-accelerating factor (DAF) as seen in in vitro studies, the binding of human complement C8 and C9 to the schistosome's paramyosin, and the attachment of C2 to the trispanning orphan receptor of Schistosoma haematobium (Sh-TOR). Ecto-enzymes on the tegument of intravascular stages including the schistosomula and adults cleave extracellular ATPs that otherwise serve as damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) as well as ADPs and inorganic polyphosphates (polyPs), thereby interfering with host pro-inflammatory and prothrombotic purinergic signaling. Eggs from the schistosomes in copula express proteases that may aid in egg egress in addition to Th2 immune responses. Granuloma formation with schistosome-induced fibrogenesis tends to limit tissue destruction brought about by egg deposition. However, disease severity is largely determined by Th17/Treg balance mediated by transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β).