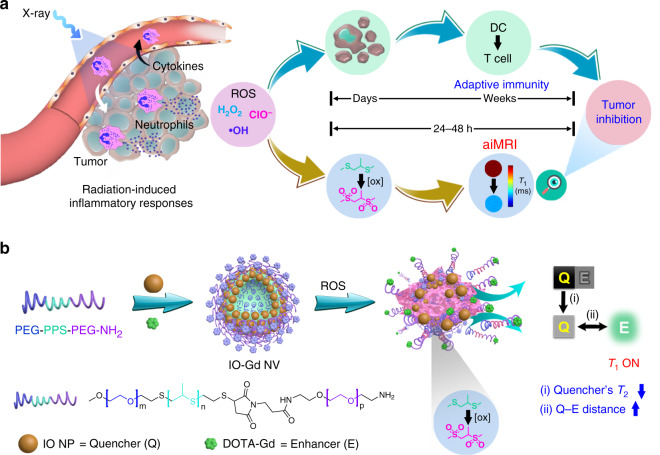
Fig. 1. Illustration of the activatable inflammation magnetic resonance imaging (aiMRI).
a Radiotherapy (RT)-induced acute inflammatory response leads to reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, which exerts tumor inhibition through ROS-induced cell apoptosis and T-cell activation pathways. The adaptive immune responses usually take days to weeks after RT. The aiMRI is applied to quantify the ROS at an early time (24–48 h) after RT which is proposed to stratify the tumor inhibition. b The procedure of self-assembly and disassembly of the aiMRI nanoprobe that is composed of iron oxide nanoparticles (IO NPs), gadolinium (Gd) species, and triblock PEG-PPS-PEG-NH2 polymers, denoted as IO-Gd NVs. The oxidation of hydrophobic thioethers to hydrophilic sulfones leads to swelling of the polymers and decomposition of the IO-Gd NVs. This procedure confers dual-positive factors to the T1 MRI OFF–ON effect: the quencher’s T2 effect is decreased upon disassembly due to the dispersed magnetic field coupling effect; (ii) the quencher-enhancer (Q-E) distance is increased due to the oxidation-induced swelling of polymers equipped with Gd species.