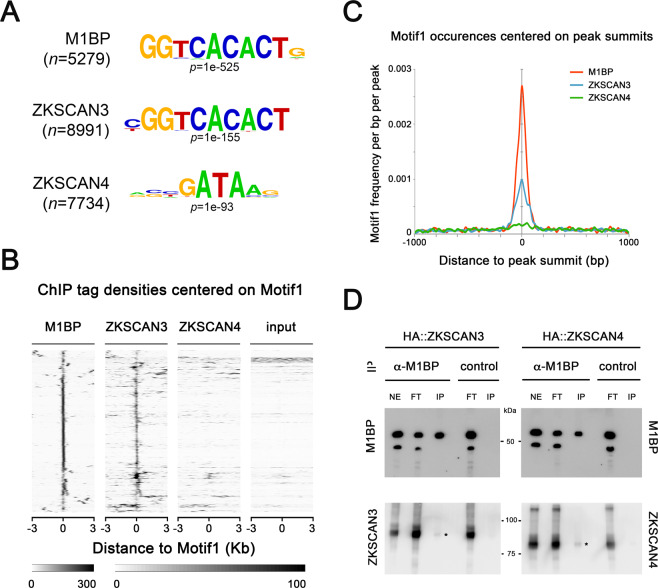
Figure 5.
ZKSCAN3 binds the same Motif 1 DNA motif as M1BP. (A) The most significant DNA sequence motif found by de novo motif discovery analyses on high confidence called peaks (1% irreproducible discovery rate) of M1BP (n = 5279 peaks), ZKSCAN3 (n = 7884 peaks), and ZKSCAN4 (n = 7734 peaks) ChIP-seq profiles shows that Motif 1 DNA element57 is significantly enriched at ZKSCAN3 and M1BP peaks. (B) Sequence tag densities of M1BP, ZKSCAN3 and ZKSCAN4 ChIP and input DNA centred on Motif1 at M1BP peaks shows that ZKSCAN3, but not ZKSCAN4 preferentially targets Motif 1 DNA sequences in Drosophila. (C) The frequency of Motif 1 position weight matrix occurrences on all M1BP, ZKSCAN3, and ZKSCAN4 ChIP peak summits show that like M1BP, Motif 1 is enriched at ZKSCAN3 ChIP peak summit binding locations. (D) ZKSCAN3 and ZKSCAN4 show little physical interaction with M1BP. M1BP was immunoprecipitated from HA::ZKSCAN3 and HA::ZKSCAN4-expressing Drosophila cell lines and probed for ZKSCAN3 or ZKSCAN4 interaction with anti-HA antisera. The low levels of both ZKSCAN3 and ZKSCAN4 interacting with M1BP (asterisks) cannot explain the ZKSCAN3-specific binding to Motif 1, since both both ZKSCAN3 and ZKSCAN4 were immunoprecipitated at equal amounts.