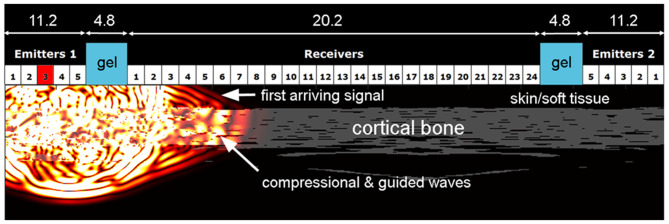
Figure 1.
Principle of bi-directional axial ultrasound transmission. The ultrasound transducer consists of two emitter arrays and one receiver array separated by gel filled gap regions (dimensions are given in mm). The numerical sound propagation simulation shows an ultrasound pulse emitted at element 3 of emitter array 1, which propagates through skin and soft tissue into the bone. One part of the wave is transmitted into the medullary canal and other parts propagate as compressional and dispersive guided waves in the axial bone direction through the cortical shell. These waves leak acoustic waves back into the soft tissue which are detected by the central receiver array.