Figure 1.
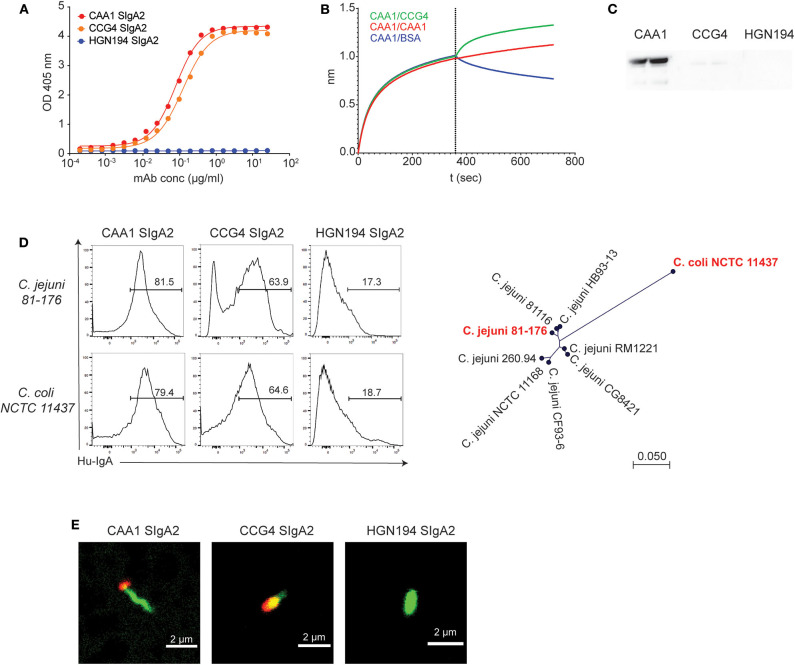
In vitro characterization of CAA1 and CCG4 secretory immunoglobulin A (SIgA) binding to FliD. (A) Binding of CAA1, CCG4, and HGN194 SIgA to recombinant FliD antigen as measure by ELISA. (B) Cross-competition studies performed by biolayer interferometry (BLI). FliD antigen was immobilized on APS sensors and then incubated with CAA1 prior to association with CCG4, CAA1, or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA). (C) Western blot analysis of CAA1, CCG4, and HGN194 SIgA binding to FliD antigen (70 kDa) under reducing and denaturing conditions. (D) Representative histograms of the in vitro binding of the indicated mAbs against pure culture of C. jejuni 81-176 (ATCC BAA-2151) and C. coli NCTC 11437. A phylogenetic tree built using neighbor-Joining method with Jukes–Cantor distance measurement is shown to provide the amino acid distance of FliD between the two historical isolates tested (in red). One representative experiment out of three is represented. (E) Binding of CAA1 SIgA to C. jejuni as observed in confocal microscopy. Bacteria were stained using Syto BC (green), whereas CAA1 was detected using anti-human IgA AF647 conjugated (red).