Figure 6.
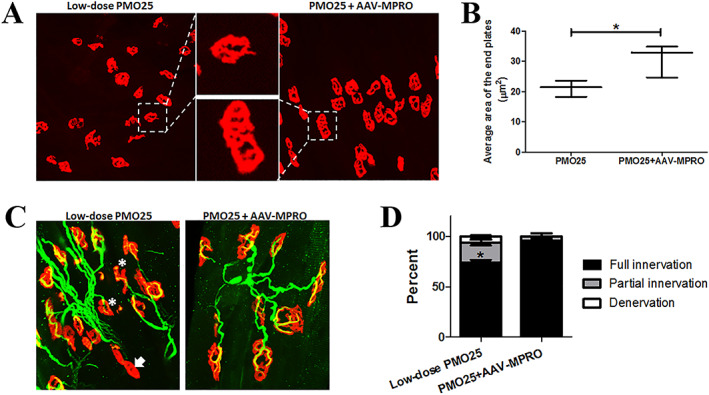
AAV‐MPRO improved NMJ maturation and innervation in low‐dose PMO25‐treated (10 μg/g) SMA mice. (A) Representative images of motor end plates, stained by α‐bungarotoxin (red), in TA muscles of 20‐day‐old SMA mice from different groups. SMA mice receiving the combinatorial treatment (PMO25 + AAV‐MPRO) showed mature morphology of the end plates, with increased length and branching of the post‐synaptic membrane and enlargement of the post‐synaptic area. (B) The areas of end plates (μm2) were quantified by ImageJ software. Over 200 end plates were assessed in each mouse. The average end plate size (μm2) was 30.82 ± 3.12 in PMO25 + AAV‐MPRO group and 21.12 ± 1.55 in mice receiving PMO25 only (n = 3 per group; P = 0.0248). (C) Representative images of NMJs in TA muscles from 20‐day‐old mice from different groups. The end plates were stained with α‐bungarotoxin (red), and the nerves were stained with anti‐neurofilament and anti‐synaptophysin (green). Asterisk indicates the partial innervation, and arrow indicates the denervation. (D) Histograms showing the quantification of fully innervated, partially innervated, and fully denervated end plates in TA muscles at PND 20 in different groups. * P < 0.05. Student's t‐test.
