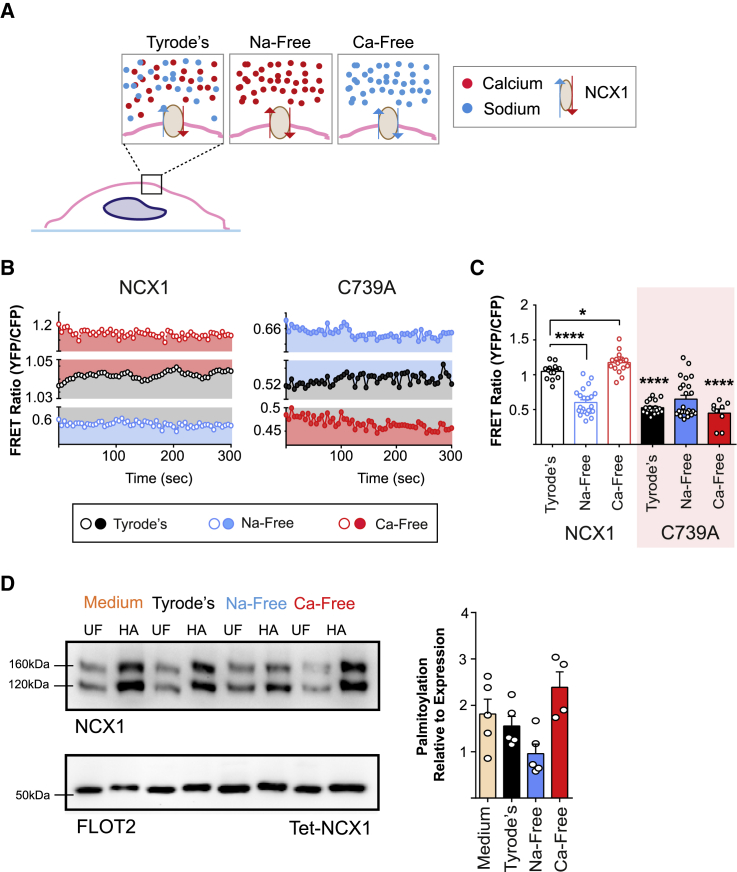
Figure 5.
NCX1 Palmitoylation and the Extracellular Environment
(A) Schematic of the experimental intervention. HEK293-expressing NCX1 FRET sensors were incubated in Tyrode’s buffer (containing physiological concentrations of Na and Ca) or modified Tyrode’s buffer that was free of either Na (replaced with NMDG) or Ca (chelated with 1 mM EGTA).
(B) An example of NCX1-NCX1 FRET measurements in transiently transfected HEK293 cells expressing WT NCX1 (left, open circles) or unpalmitoylatable NCX1 (right, closed circles) in physiological (black), sodium-free (blue) and calcium-free (red) conditions.
(C) Sodium-free (NaF) solutions reduce, and calcium-free (CaF) solutions enhance, NCX1-NCX1 FRET, but only when NCX1 is palmitoylatable. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗p = 0.01, calculated by unpaired t test. Statistical comparisons in C739A groups are to corresponding conditions for WT NCX1. N = 14 (WT, Tyrode’s), 23 (WT, Na-free), 18 (WT, Ca-free), 19 (C739A Tyrode’s), 24 (C739A Na-free), 9 (C739A, Ca-free).
(D) The same Na-free solutions reduce, and Ca-free solutions enhance, NCX1 palmitoylation. UF, unfractionated lysate; HA, purified palmitoylated fraction. The bar chart (right) shows NCX1 palmitoylation (HA fraction) normalized to expression (UF) following the indicated treatments.