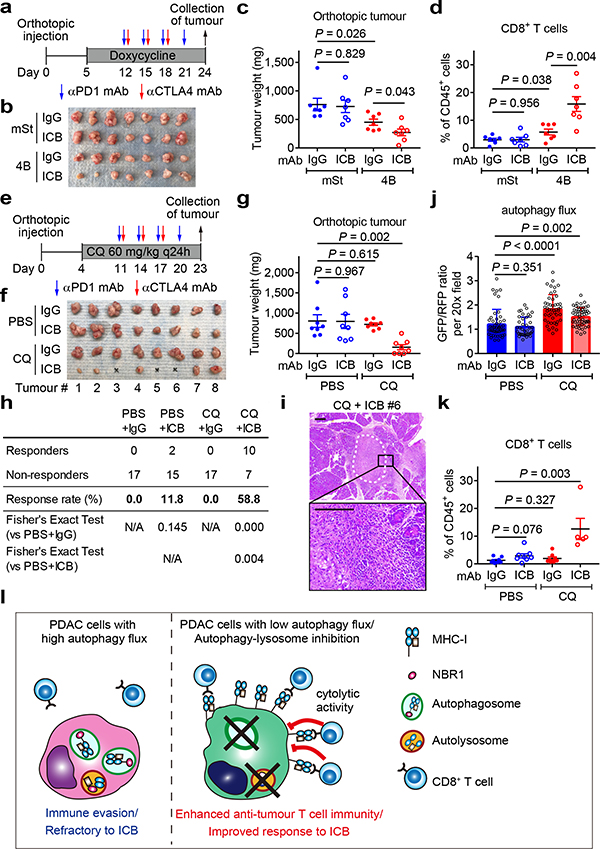
Fig. 4 |. Autophagy inhibition sensitizes PDAC to dual ICB.
a-d, Mice bearing orthotopic tumors (HY15549) expressing Dox-inducible mSt or 4B received isotype control IgG or dual ICB (anti-PD1/CTLA4 monoclonal antibodies; mAb) (n = 7 per group). Study design (a). Images (b) and weight (c) of tumours. Quantification of tumour-infiltrating CD8+ T cells by flow cytometry (d). e-k, Mice bearing orthotopic tumours (HY15549) expressing GFP-LC3-RFP reporter received CQ and ICB (n = 8 per group). Study design (e). Images (f) and weight (g) of tumours. No macroscopic tumour was identified in three animals receiving CQ + dual ICB (#3, 5, and 6). h, Response rates from two independent experiments. Response is defined as more than 80% reduction in tumour weight as compared with control tumours (PBS + IgG). i, Representative H&E images of the pancreas undergoing tumour regression (# 6). White dashed line indicates tumour remnants. Scales, 250 and 100 μm. j, Autophagy flux represented by GFP/RFP ratio per 20x field (n = 49, 39, 47 and 54; left to right). Increased GFP/RFP ratio indicates reduced autophagy flux. k, Quantification of tumour-infiltrating CD8+ T cells by flow cytometry (n = 8, 8, 8, and 5; left to right). l, In PDAC cells, surface MHC-I is downregulated by active degradation through the autophagy/lysosome system, contributing to the primary resistance to ICB. NBR1 binds to MHC-I, facilitating its trafficking to autophagosomes (left). Inhibition of autophagy or the lysosome restores surface MHC-I expression, leading to enhanced anti-tumour T cell immunity and improved response to ICB (right). Data are mean ± s.e.m. (c,d,g,k) or s.d. (j). n indicates individual mice (c,d,g,k) or individual 20x fields (j). All experiments were performed twice and representative data of one experiment are shown. P values determined by unpaired two-tailed t-tests.