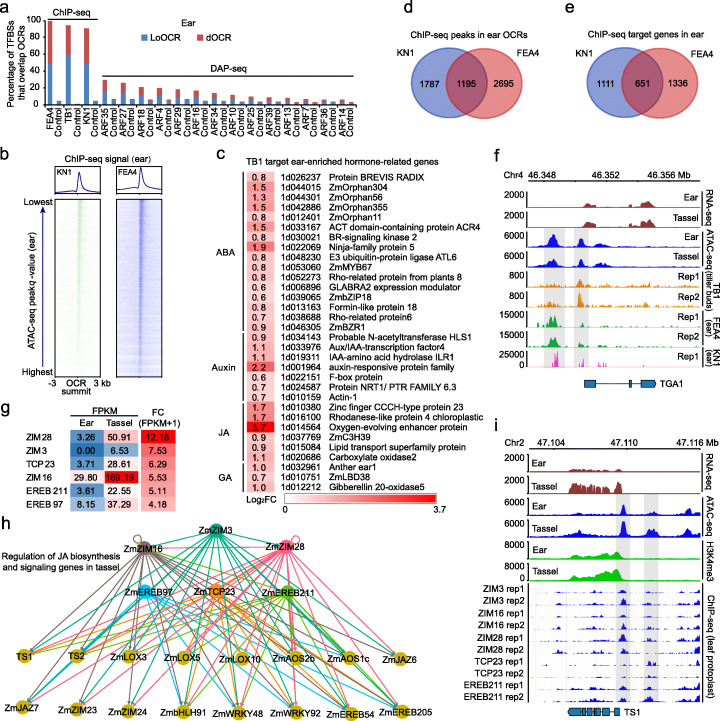
Fig. 3.
Dynamic TF binding to LoOCRs contributes to differential gene expression between ear and tassel. a Percentages of TF binding sites (TFBSs) for 3 TFs identified by in vivo ChIP-seq and TF binding sites for 14 TFs identified by in vitro DAP-seq that overlap with LoOCRs and dOCRs in ear. Controls: the same number of local and distal regions as LoOCRs and dOCRs, respectively, generated by randomly shifting dOCRs. b Distribution of the intensity of TF binding centered on ATAC-seq peak summits ordered from bottom to top by descending peak q value in ear. Shown are the regions ± 3 kb from peak summits. c Ear-enriched genes that respond to ABA, auxin, JA, and GA targeted by ear-enriched expressed TB1 identified by in vivo ChIP-seq. FC, fold change. The color scale indicates the log of fold changes in expression (log2FC). d, e Overlaps of binding sites of KN1 and FEA4 on OCRs (d) and their bound genes (e) in ear. f The OCRs near TGA1 overlapped with the potential binding sites of TB1, FEA4, and KN1. g Differential expression levels (FPKM) of 6 tassel-enriched TFs in ear and tassel. FCs (fold changes of “FPKM + 1”) are shown in ascending order in the right-hand column in the heatmap. h A proposed network of 6 tassel-enriched TFs (top two rows) and their potentially regulated genes (bottom two rows) involved in JA biosynthesis and response. These regulated genes are tassel-enriched and show more open chromatin states in tassel than in ear, except for TS2, ZmLOX5, and ZmAOS1c. ZmZIM16 and ZmZIM28 show self-binding. i A tassel-enriched gene TS1 (sex determination) shows higher chromatin accessibility and more H3K4me3 modifications in tassel than in ear. Its LoOCRs overlapped with the binding sites of 5 tassel-enriched TFs (ChIP-seq panel)